Late Roman Empire
| Roman Empire | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
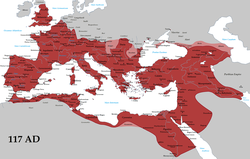
The Roman Empire in 117 AD, at its greatest extent.
|
||||||||||
| Capital |
|
|||||||||
| Languages |
|
|||||||||
| Religion |
|
|||||||||
| Government | Mixed, functionally absolute monarchy | |||||||||
| Emperor | ||||||||||
| • | 27 BC – AD 14 | Augustus (first) | ||||||||
| • | 98–117 | Trajan | ||||||||
| • | 284–305 | Diocletian | ||||||||
| • | 306–337 | Constantine I | ||||||||
| • | 379–395 | Theodosius I | ||||||||
| • | 474–480 | Julius Neposa | ||||||||
| • | 527–565 | Justinian I | ||||||||
| • | 1081–1118 | Alexius I | ||||||||
| • | 1449–1453 | Constantine XI b | ||||||||
| Legislature | Senate | |||||||||
| Historical era | Classical antiquity to Late Middle Ages | |||||||||
| • | Final War of the Roman Republic |
32–30 BC | ||||||||
| • | Empire established | 30–2 BC | ||||||||
| • | Empire at its greatest extent |
AD 117 | ||||||||
| • |
Constantinople becomes capital |
330 | ||||||||
| • | Final East West divide | 395 | ||||||||
| • | Fall of Western Empire | 476 | ||||||||
| • | Fourth Crusade | 1202–1204 | ||||||||
| • | Fall of Constantinople | 29 May 1453 | ||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||
| • | 25 BC | 2,750,000 km² (1,061,781 sq mi) | ||||||||
| • | 117 AD | 5,000,000 km² (1,930,511 sq mi) | ||||||||
| • | 390 AD | 4,400,000 km² (1,698,849 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||
| • | 25 BC est. | 56,800,000 | ||||||||
| Density | 20.7 /km² (53.5 /sq mi) | |||||||||
| Currency | Sestertius, Aureus, Solidus, Nomismac | |||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Today part of |
53 countries
|
|||||||||
|
||||||||||

Aureus of Augustus, the first Roman Emperor.
The history of the Roman Empire covers the history of Ancient Rome from the fall of the Roman Republic in 27 BC until the abdication of the last Western emperor in 476 AD. Rome had begun expanding shortly after the founding of the Republic in the 6th century BC, though it did not expand outside of the Italian Peninsula until the 3rd century BC. Civil war engulfed the Roman state in the mid 1st century BC, first between Julius Caesar and Pompey, and finally between Octavian and Mark Antony. Antony was defeated at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC. In 27 BC the Senate and People of Rome made Octavian imperator ("commander") thus beginning the Principate, the first epoch of Roman imperial history usually dated from 27 BC to 284 AD; they later awarded him the name Augustus, "the venerated". The success of Augustus in establishing principles of dynastic succession was limited by his outliving a number of talented potential heirs: the Julio-Claudian dynasty lasted for four more emperors—Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, and Nero—before it yielded in 69 AD to the strife-torn Year of Four Emperors, from which Vespasian emerged as victor. Vespasian became the founder of the brief Flavian dynasty, to be followed by the Nerva–Antonine dynasty which produced the "Five Good Emperors": Nerva, Trajan, Hadrian, Antoninus Pius and the philosophically inclined Marcus Aurelius. In the view of the Greek historian Dio Cassius, a contemporary observer, the accession of the emperor Commodus in 180 AD marked the descent "from a kingdom of gold to one of rust and iron"—a famous comment which has led some historians, notably Edward Gibbon, to take Commodus' reign as the beginning of the decline of the Roman Empire.
...
Wikipedia