Nabati
| Arabic |
العَرَبِيَّة / عَرَبِيّ
ʻarabī / al-ʻarabiyyah
|

al-ʿArabiyyah in written Arabic ( Naskh script)
|
| Pronunciation |
/ˈʕarabiː/, /ʔalʕaraˈbij.ja/
|
| Native to |
Countries of the Arab League, minorities in neighboring countries and some parts of Asia,Africa, Europe etc. |
|
Native speakers
|
290 million (2017) |
|
|
|
|
Standard forms
|
|
| Dialects |
|
|
|
Arabic alphabet
Arabic Braille
Syriac alphabet (Garshuni)
Hebrew alphabet (Judeo-Arabic languages)
Greek alphabet (Cypriot Maronite Arabic)
Latin script (Romanization of Arabic, Maltese alphabet) (Maltese, Lebanese Arabic, Moroccan Arabic, Libyan Arabic, Tunisian Arabic) |
|
|
Signed Arabic (national forms) |
| Official status |
|
Official language in
|
Modern Standard Arabic is an official language of 28 states, the third most after English and French
|
| Regulated by |
|
| Language codes |
| ISO 639-1 |
ar |
| ISO 639-2 |
|
| ISO 639-3 |
Individual codes:
arq – Algerian Arabic
aao – Algerian Saharan Arabic
bbz – Babalia Creole Arabic
aby – Baharna Arabic
shu – Chadian Arabic
acy – Cypriot Arabic
adf – Dhofari Arabic
avl – Eastern Egyptian Bedawi Arabic
arz – Egyptian Arabic
afb – Gulf Arabic
ayh – Hadrami Arabic
acw – Hijazi Arabic
ayl – Libyan Arabic
acm – Mesopotamian Arabic
ary – Moroccan Arabic
ars – Najdi Arabic
apc – North Levantine Arabic
ayp – North Mesopotamian Arabic
acx – Omani Arabic
aec – Saidi Arabic
ayn – Sanaani Arabic
ssh – Shihhi Arabic
ajp – South Levantine Arabic
arb – Standard Arabic
apd – Sudanese Arabic
pga – Sudanese Creole Arabic
acq – Taizzi-Adeni Arabic
abh – Tajiki Arabic
aeb – Tunisian Arabic
auz – Uzbeki Arabic
|
| Glottolog |
arab1395 |
| Linguasphere |
12-AAC |
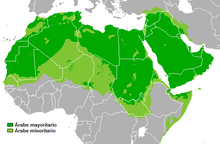
Dispersion of native Arabic speakers as the majority (green) or minority (chartreuse) population
|
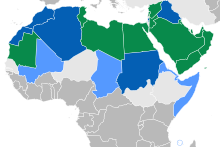
Use of Arabic as the national language (green), as an official language (dark blue), and as a regional/minority language (light blue)
|
|
This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Unicode characters. |
Arabic (Arabic: العَرَبِيَّة, al-ʻarabiyyah [ʔalʕaraˈbij.ja] or Arabic: عَرَبِيّ ʻarabī [ˈʕarabiː, ʕaraˈbij]) is a Central Semitic language that was first spoken in Iron Age northwestern Arabia and is now the lingua franca of the Arab world. Arabic is also the liturgical language of 1.7 billion Muslims. It is one of six official languages of the United Nations. It is named after the Arabs, a term initially used to describe peoples living from Mesopotamia in the east to the Anti-Lebanon mountains in the west, and from northwestern Arabia to the Sinai in the south.
Arabic is considered, in its standard form and dialects, a single language; it is spoken by perhaps as many as 422 million speakers (native and non-native) in the Arab world, making it one of the five most spoken languages in the world.
The modern written language (Modern Standard Arabic) is derived from the language of the Quran (known as Classical Arabic or Quranic Arabic). It is widely taught in schools and universities, and is used to varying degrees in workplaces, government, and the media. The two formal varieties are grouped together as Literary Arabic, which is the official language of 26 states and the liturgical language of Islam. Modern Standard Arabic largely follows the grammatical standards of Quranic Arabic and uses much of the same vocabulary. However, it has discarded some grammatical constructions and vocabulary that no longer have any counterpart in the spoken varieties, and has adopted certain new constructions and vocabulary from the spoken varieties. Much of the new vocabulary is used to denote concepts that have arisen in the post-Quranic era, especially in modern times.
...
Wikipedia



