BZIP domain
| bZIP transcription factor | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
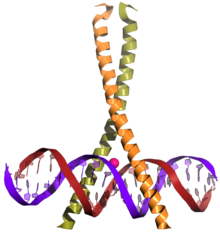
CREB (top) is a transcription factor capable of binding DNA via the bZIP domain (bottom) and regulating gene expression.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | bZIP_1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00170 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR011616 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00036 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1ysa | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1ysa | ||||||||
| CDD | cd14686 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain (bZIP domain) is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required to hold together (dimerize) two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic amino acids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containing this domain are transcription factors.
bZIP transcription factors are found in all organisms. An evolutionary study from 2008 revealed that 4 bZIP genes were encoded by the genome of the most recent common ancestor of all plants. Interactions between bZIP transcription factors play important roles in cancer development in epithelial tissues, steroid hormone synthesis by cells of endocrine tissues, factors affecting reproductive functions, and several other phenomena that affect human health.
ATF1; ATF2; ATF4; ATF5; ATF6; ATF7; BACH1; BACH2; BATF; BATF2; CEBPA; CREB1; CREB3; CREB3L1; CREB3L2; CREB3L3; CREB3L4; CREB5; CREBL1; CREM; E4BP4; FOSL1; FOSL2; JUN; JUNB; JUND; MAFA; MAFB; NFE2; NFE2L2; NFE2L3; SNFT; XBP1
...
Wikipedia
