French Language
| French | |
|---|---|
| français | |
| Pronunciation | [fʁɑ̃sɛ] |
| Native to |
France, now worldwide (See geographical distribution below) |
|
Native speakers
|
80 million (2016) 274 million total speakers (2014) |
|
Early forms
|
Old French
|
|
Latin (French alphabet) French Braille |
|
|
Signed French (français signé) |
|
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
Numerous international organisations |
| Regulated by | Académie française (French Academy) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | fr |
| ISO 639-2 |
(B) (T)
|
| ISO 639-3 | |
| Glottolog | stan1290 |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-i |
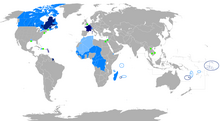
Regions where French is the main language
Regions where it is an official language
Regions where it is a second language
Regions where it is a minority language
|
|
French (le français [lə fʁɑ̃sɛ] or la langue française [la lɑ̃ɡ fʁɑ̃sɛz]) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did languages such as Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, Romanian, Catalan and others. French has evolved from Gallo-Romance, the spoken Latin in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) has largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as "Francophone" in both English and French.
...
Wikipedia
