Rhodanase
| Rhodanese-like domain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Rhodanese | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00581 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001763 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00322 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 2ora | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 2ora | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
Rhodanese, also known as rhodanase, thiosulfate sulfurtransferase, thiosulfate cyanide transsulfurase, and thiosulfate thiotransferase, is a enzyme that detoxifies cyanide (CN−) by converting it to thiocyanate (SCN−).
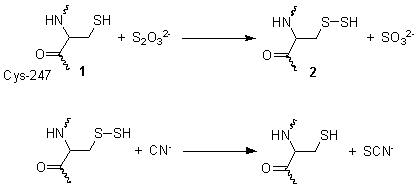
This reaction takes place in two steps. The diagram on the right shows the crystallographically-determined structure of rhodanese. In the first step, thiosulfate is reduced by the thiol group on cysteine-247 1, to form a persulfide and a sulfite 2. In the second step, the persulfide reacts with cyanide to produce thiocyanate, re-generating the cysteine thiol 1.
This reaction is important for the treatment of exposure to cyanide, since the thiocyanate formed is less toxic. The use of thiosulfate solution as an antidote for cyanide poisoning is based on the activation of this enzymatic cycle.
Rhodanese shares evolutionary relationship with a large family of proteins, including
Rhodanese has an internal duplication. This domain is found as a single copy in other proteins, including phosphatases and ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases.
CDC25A; CDC25B; CDC25C; DUSP; DUSP1; DUSP10; DUSP16; DUSP2; DUSP4; DUSP5; DUSP6; DUSP7; KAT; MKP7; MOCS3; MPST; TBCK; TSGA14; TST; USP8;
...
Wikipedia