Ancient Roman Republic
| Roman Republic | ||||||||||||||||
|
Official name (as on coins): Roma after c. 100 BC: Senatus populusque Romanus (Latin) (SPQR) ("The Senate and People of Rome") |
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Roman provinces on the eve of the assassination of Julius Caesar, 44 BC
|
||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Rome | |||||||||||||||
| Languages |
Latin (official), various unofficial spoken in certain places including Etruscan, Greek, Hebrew, Aramaic, Syriac, Gallic, Punic, Berber, Iberian |
|||||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman polytheism | |||||||||||||||
| Government | Republic | |||||||||||||||
| Consul | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 509–508 BC |
Lucius Brutus, Lucius Collatinus |
||||||||||||||
| • | 27 BC |
Gaius Octavianus, Marcus Agrippa |
||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Legislative Assemblies | |||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Classical antiquity | |||||||||||||||
| • | Overthrow of Tarquinius Superbus following the Rape of Lucretia | 509 BC | ||||||||||||||
| • | Caesar proclaimed dictator for 10 years | 47 BC | ||||||||||||||
| • | Battle of Actium | 2 September 31 BC | ||||||||||||||
| • | Octavian proclaimed Augustus | 16 January 27 BC | ||||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 326 BC | 10,000 km2 (3,900 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| • | 200 BC | 360,000 km2 (140,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| • | 146 BC | 800,000 km2 (310,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| • | 100 BC | 1,200,000 km2 (460,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| • | 50 BC | 1,950,000 km2 (750,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Currency | Roman Republican currency | |||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Today part of |
33 countries
|
|||||||||||||||

Roman consul accompanied by two lictors
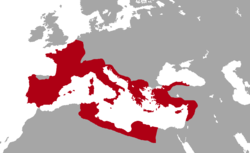
The Roman Republic (Latin: Res publica Romana; Classical Latin: [ˈreːs ˈpuːb.lɪ.ka roːˈmaː.na]) was the era of ancient Roman civilization beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom, traditionally dated to 509 BC, and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire. It was during this period that Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world.
During the first two centuries of its existence, the Roman Republic expanded through a combination of conquest and alliance, from central Italy to the entire Italian peninsula. By the following century, it included North Africa, most of the Iberian Peninsula, and what is now southern France. Two centuries after that, towards the end of the 1st century BC, it included the rest of modern France, Greece, and much of the eastern Mediterranean. By this time, internal tensions led to a series of civil wars, culminating with the assassination of Julius Caesar, which led to the transition from republic to empire.
...
Wikipedia