Maiz
| Maize | |
|---|---|
 |
|
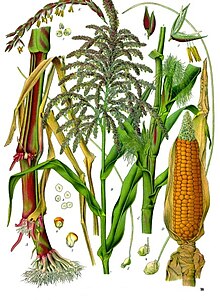
| Illustration depicting both male and female flowers of maize | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Monocots |
| (unranked): | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Subfamily: | Panicoideae |
| Tribe: | Andropogoneae |
| Genus: | Zea |
| Species: | Z. mays |
| Subspecies: | Z. mays subsp. mays |
| Trinomial name | |
|
Zea mays subsp. mays L. |
|
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 360 kJ (86 kcal) |
|
18.7 g
|
|
| Starch | 5.7 g |
| Sugars | 6.26 g |
| Dietary fiber | 2 g |
|
1.35 g
|
|
|
3.27 g
|
|
| Tryptophan | 0.023 g |
| Threonine | 0.129 g |
| Isoleucine | 0.129 g |
| Leucine | 0.348 g |
| Lysine | 0.137 g |
| Methionine | 0.067 g |
| Cystine | 0.026 g |
| Phenylalanine | 0.150 g |
| Tyrosine | 0.123 g |
| Valine | 0.185 g |
| Arginine | 0.131 g |
| Histidine | 0.089 g |
| Alanine | 0.295 g |
| Aspartic acid | 0.244 g |
| Glutamic acid | 0.636 g |
| Glycine | 0.127 g |
| Proline | 0.292 g |
| Serine | 0.153 g |
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A equiv. |
(1%)
9 μg
644 μg
|
| Thiamine (B1) |
(13%)
0.155 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(5%)
0.055 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(12%)
1.77 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
(14%)
0.717 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(7%)
0.093 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(11%)
42 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(8%)
6.8 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Iron |
(4%)
0.52 mg |
| Magnesium |
(10%)
37 mg |
| Manganese |
(8%)
0.163 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(13%)
89 mg |
| Potassium |
(6%)
270 mg |
| Zinc |
(5%)
0.46 mg |
| Other constituents | |
| Water | 75.96 g |
|
Link to USDA Database entry
One ear of medium size (6-3/4" to 7-1/2" long) maize has 90 grams of seeds |
|
|
|
| Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|
Maize (/ˈmeɪz/ MAYZ; Zea mays subsp. mays, from Spanish: maíz after Taíno mahiz), also known as corn, is a large grain plant first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago.The leafy stalk of the plant produces separate pollen and ovuliferous inflorescences or ears, which are fruits, yielding kernels or seeds.
Maize has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with that of wheat or rice. However not all of this maize is consumed directly by humans. Some of the maize production is used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and corn syrup. The six major types of corn are dent corn, flint corn, pod corn, popcorn, flour corn, and sweet corn.
...
Wikipedia
