Glycine
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Glycine
|
|||
| Other names
Aminoethanoic acid
Aminoacetic acid Glycocoll |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
56-40-6 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| Abbreviations | Gly, G | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:15428 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL773 |
||
| ChemSpider |
730 |
||
| DrugBank |
DB00145 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.248 | ||
| EC Number | 200-272-2 | ||
| 727 | |||
| KEGG |
D00011 |
||
| PubChem | 750 | ||
| UNII |
TE7660XO1C |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C2H5NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 75.07 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Density | 1.607 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 233 °C (451 °F; 506 K) (decomposition) | ||
| 24.99 g/100 mL (25 °C) | |||
| Solubility | soluble in pyridine sparingly soluble in ethanol insoluble in ether |
||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.34 (carboxyl), 9.6 (amino) | ||
| -40.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Pharmacology | |||
| B05CX03 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | See: data page | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
2600 mg/kg (mouse, oral) | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
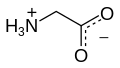
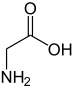
Glycine (abbreviated as Gly or G) is the amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest possible amino acid. The chemical formula of glycine is NH2‐CH2‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG of the genetic code.
Glycine is a colorless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid. It is unique among the proteinogenic amino acids in that it is achiral. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments since it exists as zwitterion at natural pH, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. The acyl radical is glycyl.
Glycine was first isolated from gelatin in 1820. The name comes from the ancient Greek word γλυκύς "sweet tasting" (which is also related to the prefixes and , as in glycoprotein and glucose).
Glycine was discovered in 1820, by Henri Braconnot who boiled a gelatinous object with sulfuric acid.
Glycine is manufactured industrially by treating chloroacetic acid with ammonia:
About 15 million kg are produced annually in this way.
...
Wikipedia