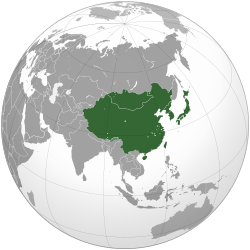
Eastern Asia
| East Asia |
 |
| States and territories |
|
| Capital cities |
|
| Major cities |
|
| Area
|
| • Total |
11,839,074 km2 (4,571,092 sq mi) |
| Population
|
| • Total |
1,601,709,712 |
| • Density |
140/km2 (350/sq mi) |
| Time zone |
- UTC +7:00 (Western Mongolia)
- UTC +8:00 (Rest of Mongolia, Mainland China, Taiwan, Macau and Hong Kong)
- UTC +8:30 (North Korea)
- UTC +9:00 (Japan and South Korea)
|
| Languages and language families |
|
East Asia is the eastern subregion of the Asian continent, which can be defined in either geographical or ethno-cultural terms. Geographically and geopolitically, it includes China, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan; Mongolia, Korea (North and South) and Japan; it covers about 12,000,000 km2 (4,600,000 sq mi), or about 28% of the Asian continent, about twice the area of Europe.
The East Asian people comprise more than 1.5 billion people. About 38% of the population of Asia and 22%, or over one fifth, of all the people in the world live in East Asia. Although the coastal and riparian areas of the region form one of the world's most populated places, the population in Mongolia and Western China, both landlocked areas, is very sparsely distributed, with Mongolia having the lowest population density of a sovereign state. The overall population density of the region is 133 inhabitants per square kilometre (340/sq mi), about three times the world average of 45/km2 (120/sq mi).
Historically, societies in East Asia have been part of the Chinese cultural sphere, and East Asian vocabulary and scripts are often derived from Classical Chinese and Chinese script. Major religions include Buddhism (mostly Mahayana), Confucianism or Neo-Confucianism, Taoism, Chinese folk religion in China and Taiwan, Shinto in Japan, Korean shamanism in Korea. Shamanism is also prevalent among Mongolians and other indigenous populations of northern East Asia. The Chinese calendar is the root from which many other East Asian calendars are derived.
...
Wikipedia

