Chinese morphology
| Chinese | |
|---|---|
| 汉语/漢語 Hànyǔ or 中文 Zhōngwén | |

Hànyǔ (Chinese) written in traditional (top), simplified (middle) characters and alternative name (bottom)
|
|
| Native to | People's Republic of China, Republic of China (Taiwan), Singapore |
| Ethnicity | Han Chinese |
|
Native speakers
|
1.2 billion (2004) |
|
Sino-Tibetan
|
|
|
Early forms
|
|
|
Standard forms
|
|
| Dialects | |
|
Simplified Chinese Traditional Chinese Transcriptions: Zhuyin Pinyin (Latin) Xiao'erjing (Arabic) Dungan (Cyrillic) 'Phags-pa script (Historical) |
|
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
|
| Regulated by | National Commission on Language and Script Work (Mainland China) National Languages Committee (Taiwan) Civil Service Bureau (Hong Kong) Promote Mandarin Council (Singapore) Chinese Language Standardisation Council (Malaysia) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | zh |
| ISO 639-2 |
chi (B)zho (T)
|
| ISO 639-3 |
Individual codes: |
| Glottolog | sini1245 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA |
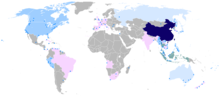
Map of the Sinophone world
Legend:
Countries identified Chinese as a primary, administrative, or native language
Countries with more than 5,000,000 Chinese speakers
Countries with more than 1,000,000 Chinese speakers
Countries with more than 500,000 Chinese speakers
Countries with more than 100,000 Chinese speakers
Major Chinese-speaking settlements
|
|
| Chinese languages (Spoken) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Han language | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese language (Written) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Middle/Central/Chinese text | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend:
Chinese (simplified Chinese: 汉语; traditional Chinese: 漢語; pinyin: Hànyǔ; literally: "Han language"; or Chinese: 中文; pinyin: Zhōngwén; literally: "Chinese writing") is a group of related, but in many cases mutually unintelligible, language varieties, forming a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Chinese is spoken by the Han majority and many minority ethnic groups in China. About 1.2 billion people (around 16% of the world's population) speak some form of Chinese as their first language.
The varieties of Chinese are usually described by native speakers as dialects of a single Chinese language, but linguists note that they are as diverse as a language family. The internal diversity of Chinese has been likened to that of the Romance languages, but may be even more varied. There are between 7 and 13 main regional groups of Chinese (depending on classification scheme), of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (about 960 million, e.g. Southwestern Mandarin), followed by Wu (80 million, e.g. Shanghainese), Min (70 million, e.g. Southern Min), Yue (60 million, e.g. Cantonese), etc. Most of these groups are mutually unintelligible, and even dialect groups within Min Chinese may not be mutually intelligible. Some, however, like Xiang and certain Southwest Mandarin dialects, may share common terms and a certain degree of intelligibility. All varieties of Chinese are tonal and analytic.
...
Wikipedia
