Seleucid Syria
| Seleucid Empire | ||||||||||||||||||
| Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν | ||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
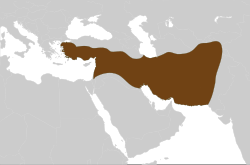
The empire at its greatest extent and on the eve of the death of Seleucus I, 281 BC
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Capital |
Seleucia (305–240 BC) Antioch (240–63 BC) |
|||||||||||||||||
| Languages |
Greek (official) Persian Aramaic |
|||||||||||||||||
| Religion |
Olympianism Babylonian religion Zoroastrianism |
|||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | |||||||||||||||||
| Basileus | ||||||||||||||||||
| • | 305–281 BC | Seleucus I (first) | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 65–63 BC | Philip II (last) | ||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Hellenistic period | |||||||||||||||||
| • | Wars of the Diadochi | 312 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| • | Battle of Ipsus | 301 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| • | Roman–Seleucid War | 192–188 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| • | Treaty of Apamea | 188 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| • | Maccabean Revolt | 167–160 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| • | Annexed by Rome | 63 BC | ||||||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||||||
| • | 303 BC | 3,000,000 km² (1,158,306 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 301 BC | 3,900,000 km² (1,505,798 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 270 BC | 3,200,000 km² (1,235,527 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 240 BC | 2,600,000 km² (1,003,866 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| • | 175 BC | 800,000 km² (308,882 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||

Tetradrachm of Seleucus I, the horned horse, the elephant and the anchor were all used as symbols of the Seleucid monarchy.
The Seleucid Empire (/sɪˈljuːsɪd/;Ancient Greek: Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, Basileía tōn Seleukidōn) was a Hellenistic state ruled by the Seleucid dynasty, which existed from 312 BC to 63 BC; it was founded by Seleucus I Nicator following the division of the Macedonian empire vastly expanded by Alexander the Great. Seleucus received Babylonia and, from there, expanded his dominions to include much of Alexander's near eastern territories. At the height of its power, it included central Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and what is now Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Pakistan and Turkmenistan.
...
Wikipedia