Danish Language
| Danish | |
|---|---|
| dansk | |

The first page of the Jutlandic Law originally from 1241 in Codex Holmiensis, copied in 1350.
The first sentence is: "Mædh logh skal land byggas" Modern orthography: "Med lov skal land bygges" English translation: "With law shall a country be built" |
|
| Pronunciation | [d̥anˀsɡ̊] |
| Native to | |
|
Native speakers
|
5.5 million (2012) |
|
Indo-European
|
|
|
Early forms
|
|
| Dialects | |
|
Latin script: Dano-Norwegian alphabet ∙ Danish orthography ∙ Danish Braille |
|
| Danish Sign Language | |
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
|
|
Recognised minority
language in |
|
| Regulated by | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | da |
| ISO 639-2 | |
| ISO 639-3 | Either: dan – Insular Danish jut – Jutlandic |
| Glottolog | dani1284 |
| Linguasphere | 5 2-AAA-bf & -ca to -cj |
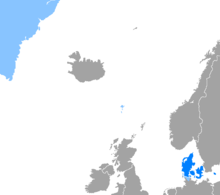
The Danish-speaking world:
regions where Danish is the language of the majority
regions where Danish is the language of a significant minority, or (in the case of Iceland), taught as 2nd or 3rd language to a majority)
|
|
Danish ![]() i/ˈdeɪnᵻʃ/ (dansk pronounced [d̥anˀsɡ̊]; dansk sprog, [ˈd̥anˀsɡ̊ ˈsb̥ʁɔʊ̯ˀ]) Dansk is a language spoken by around six million people, principally in Denmark. There are also minor Danish-speaking communities in Norway, Sweden, Spain, the United States, Canada, Brazil and Argentina. Due to immigration and language shift in urban areas, around 15–20% of the population of Greenland speak Danish as their home language.
i/ˈdeɪnᵻʃ/ (dansk pronounced [d̥anˀsɡ̊]; dansk sprog, [ˈd̥anˀsɡ̊ ˈsb̥ʁɔʊ̯ˀ]) Dansk is a language spoken by around six million people, principally in Denmark. There are also minor Danish-speaking communities in Norway, Sweden, Spain, the United States, Canada, Brazil and Argentina. Due to immigration and language shift in urban areas, around 15–20% of the population of Greenland speak Danish as their home language.
Along with the other North Germanic languages, Danish is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples that lived in Scandinavia during the Viking Era. Danish, together with Swedish, derives from the East Norse dialect group, while the Middle Norwegian language before the influence of Danish and Norwegian Bokmål are classified as West Norse along with Faroese and Icelandic. A more recent classification based on mutual intelligibility separates modern spoken Danish, Norwegian and Swedish as Mainland Scandinavian while Icelandic and Faroese are classified as Insular Scandinavian.
...
Wikipedia
