1938 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1938 Atlantic hurricane season |

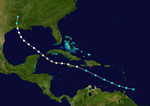
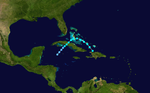
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
January 3, 1938 (record earliest)
|
| Last system dissipated |
November 10, 1938 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
"Great New England" |
| • Maximum winds |
160 mph (260 km/h) |
| • Lowest pressure |
940 mbar (hPa; 27.76 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
15 |
| Total storms |
9 |
| Hurricanes |
4 |
Major hurricanes
(Cat. 3+) |
2 |
| Total fatalities |
701 |
| Total damage |
$290.3 million (1938 USD) |
|
|
Atlantic hurricane seasons
1936, 1937, 1938, 1939, 1940
|
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
January 3 – January 6 |
| Peak intensity |
80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 992 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 8 – August 9 |
| Peak intensity |
70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) 1002 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 10 – August 15 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) 995 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 23 – August 29 |
| Peak intensity |
120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 964 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 9 – September 14 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1009 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 9 – September 22 |
| Peak intensity |
160 mph (260 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 940 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 10 – October 17 |
| Peak intensity |
60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 16 – October 21 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1004 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 6 – November 10 |
| Peak intensity |
70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 1000 mbar (hPa) |
The 1938 Atlantic hurricane season was a period of annual tropical cyclone formation in the Atlantic, lasting from June 16 through October 31. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin.
On January 1, a weak extratropical cyclone formed about 2,000 miles (3,200 km) southwest of the island of São Miguel in the Azores. Moving eastward initially, it later began a turn to the south on January 3. On that day, the cyclone transitioned into a warm-core system, a tropical storm with winds of 60 miles per hour (97 km/h). Henceforth, it gradually curved to the southwest and on January 4 became a hurricane, equal to Category 1 on the modern Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale. It peaked at 80 mph (130 km/h) that same day but weakened into a tropical storm on January 5. Turning to the south-southwest, it dissipated on January 6 while centered well to the east of the Lesser Antilles. The cyclone became the first documented Atlantic tropical cyclone to attain hurricane intensity in the month of January and is one of just six Atlantic storms known to have occurred in that month, the others being a tropical storm in 1951, Hurricane Alice in 1955, a subtropical storm in 1978, Tropical Storm Zeta in 2006 and Hurricane Alex in 2016.
...
Wikipedia