1936 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1936 Atlantic hurricane season |
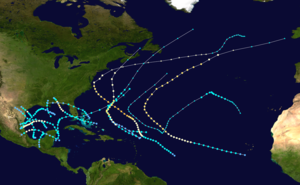
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
June 12, 1936 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 6, 1936 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
Thirteen |
| • Maximum winds |
120 mph (195 km/h) |
| • Lowest pressure |
962 mbar (hPa; 28.41 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
20 |
| Total storms |
17 |
| Hurricanes |
7 |
Major hurricanes
(Cat. 3+) |
1 |
| Total fatalities |
5 total |
| Total damage |
~ $1.23 million (1936 USD) |
|
|
Atlantic hurricane seasons
1934, 1935, 1936, 1937, 1938
|
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 12 – June 17 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 996 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 19 – June 22 |
| Peak intensity |
50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min) 1000 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 26 – June 28 |
| Peak intensity |
80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) 987 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 26 – July 28 |
| Peak intensity |
45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min) 1003 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 27 – August 1 |
| Peak intensity |
105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 964 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 4 – August 9 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1001 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 7 – August 12 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1008 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 15 – August 20 |
| Peak intensity |
75 mph (120 km/h) (1-min) 999 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 20 – August 23 |
| Peak intensity |
60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 1002 mbar (hPa) |
The 1936 Atlantic hurricane season officially began on June 12, 1936, and lasted until December 6, 1936. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin.
The 1936 season was fairly active, with 20 tropical cyclones including 3 tropical depressions. Seven storms became hurricanes, of which one became a major hurricane. In addition, the season was unusual in the fact that no storms moved across large portions of the Caribbean Sea. Seven storms, including three hurricanes, struck the United States. The season also set many records for the earliest date for a numbered storm, though all were surpassed by the extreme activity of the 2005 season.
On June 9, a tropical cyclone with atmospheric pressure below 988 millibars (29.18 inHg) made landfall on the Pacific coast of Guatemala. It moved northeastward across Central America, but dissipated before reaching the western Caribbean Sea on June 12. The storm quickly re-organized, and again developed into a tropical storm on June 12. It moved north-northeastward, resulting in light winds as it paralleled the eastern coasts of Belize and the Yucatán Peninsula. After reaching the Gulf of Mexico with peak winds of 45 miles per hour (72 km/h), the storm turned to the northeast, then to the east. On June 15, the tropical storm made landfall about 20 miles (32 km) to the south of Fort Myers, Florida, and after crossing the state it passed over Miami before entering the Atlantic Ocean. It weakened as it accelerated northeastward through the Bahamas, and on June 17 the system dissipated to the north of Bermuda.
...
Wikipedia










