Warfarin overdose
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈwɔːrfəˌrɪn/ WORF-ə-rin |
| Trade names | Coumadin, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682277 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth or intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 79-100% (by mouth) |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Liver: CYP2C9, 2C19, 2C8, 2C18, 1A2 and 3A4 |
| Biological half-life | 20-60 hours (mean: 40 hours) |
| Excretion | Kidney (92%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.253 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
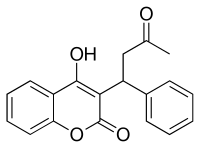
| Formula | C19H16O4 |
| Molar mass | 308.33 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to treat blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism and to prevent stroke in people who have atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease or artificial heart valves. Less commonly it is used following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and orthopedic surgery. It is generally taken by mouth but may also be used by injection into a vein.
The common side effect is bleeding. Less common side effects may include areas of tissue damage and purple toes syndrome. Use is not generally recommended during pregnancy. It is recommended that the effects of warfarin typically be monitored by checking prothrombin time (INR) every one to four weeks. Many other medications and dietary factors can interact with warfarin, either increasing or decreasing its effectiveness. The effects of warfarin may be reversed with phytonadione (vitamin K1), fresh frozen plasma, or prothrombin complex concentrate.
Warfarin decreases blood clotting by blocking an enzyme called vitamin K epoxide reductase that reactivates vitamin K1. Without sufficient active vitamin K1, clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X have decreased clotting ability. The anticlotting protein C and protein S are also inhibited but to a lesser degree. A few days are required for full effect to occur and these effects can last for up to five days.
...
Wikipedia
