Sufyanids
| Umayyad Caliphate | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
الخلافة الأموية Al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawiyyah (Arabic) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
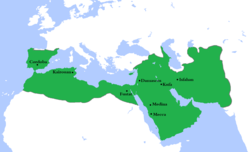
The Umayyad Caliphate at its greatest extent
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital |
Damascus (661–744) Harran (744–750) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital-in-exile |
Córdoba (756–1031) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Languages | Arabic (official) – Coptic, Greek, Latin, Persian (official in certain regions until the reign of Abd al-Malik) – Aramaic, Armenian, Berber language, African Romance, Mozarabic, Sindhi language, Georgian, Prakrit | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Caliphate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Caliph | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | 661–680 | Muawiya I | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • | 743–744 | Al-Walid II | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • | 744–750 | Marwan II | ||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | Muawiya becomes Caliph | estimated from 660 to 665 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| • | Defeat and death of Marwan II by the Abbasids | 750 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | AD 720 | 11,100,000 km² (4,285,734 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| • | 750 (132 AH) est. | 34,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Gold dinar and dirham | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
The Umayyad Caliphate (Arabic: الخلافة الأموية, trans. Al-Khilāfah al-ʾumawiyya), also spelled Omayyad, was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. This caliphate was centred on the Umayyad dynasty (Arabic: الأمويون, al-ʾUmawiyyūn, or بنو أمية, Banū ʾUmayya, "Sons of Umayya"), hailing from Mecca. The Umayyad family had first come to power under the third caliph, Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), but the Umayyad regime was founded by Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Syria, after the end of the First Muslim Civil War in AD 661/41 AH. Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, and Damascus was their capital. The Umayyads continued the Muslim conquests, incorporating the Caucasus, Transoxiana, Sindh, the Maghreb and the Iberian Peninsula (Al-Andalus) into the Muslim world. At its greatest extent, the Umayyad Caliphate covered 11,100,000 km2 (4,300,000 sq mi) and 62 million people (29% of the world's population), making it one of the largest empires in history in both area and proportion of the world's population.
...
Wikipedia