Republic of China (mainland)
| Republic of China | ||||||||||||||
|
中華民國 Chunghwa Minkuo |
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
Anthem
|
||||||||||||||
|
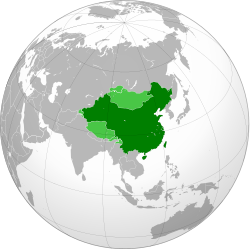
Location and maximum extent of the territory claimed by the Republic of China.
|
||||||||||||||
| Capital | ||||||||||||||
| Languages |
Chinese Tibetan Chagatai/Uighur Manchu Mongolian and other languages |
|||||||||||||
| Demonym | Chinese | |||||||||||||
| Government |
Federal semi-presidential republic under Beiyang rule (1912–15, 1916–28) One-party state under a military dictatorship (1928–49) |
|||||||||||||
| President | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1912 |
Sun Yat-sen (first) (provisional) |
||||||||||||
| • | 1949 |
Li Zongren (last) (acting) |
||||||||||||
| Premier | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1912 | Tang Shaoyi (first) | ||||||||||||
| • | 1949 | He Yingqin (last) | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | 20th century | |||||||||||||
| • | Republic proclaimed | 1 January 1912 | ||||||||||||
| • | Monarchy abolished | 12 February 1912 | ||||||||||||
| • | Beiyang rule from Peking | 10 October 1912 | ||||||||||||
| • | Nationalist rule from Nanking | 18 April 1927 | ||||||||||||
| • | Second Sino-Japanese War | 7 July 1937–2 September 1945 | ||||||||||||
| • | United Nations admission | 25 October 1945 | ||||||||||||
| • | People's Republic of China proclaimed | 1 October 1949 | ||||||||||||
| • | Kuomintang Government flee to Taipei, Taiwan | 7 December 1949 | ||||||||||||
| Area | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1912 | 11,077,380 km2 (4,277,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| • | 1946 | 9,676,204 km2 (3,736,003 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Population | ||||||||||||||
| • | 1912 est. | 432,375,000 | ||||||||||||
| Density | 39/km2 (101/sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| • | 1920 est. | 472,000,000 | ||||||||||||
| Density | 43/km2 (110/sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| • | 1930 est. | 489,000,000 | ||||||||||||
| Density | 44/km2 (114/sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| • | 1946 est. | 535,418,000 | ||||||||||||
| Density | 55/km2 (143/sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| • | 1949 est. | 541,670,000 | ||||||||||||
| Density | 56/km2 (145/sq mi) | |||||||||||||
| Currency | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
| a. | 1912 and 1927–49 (although see footnote c immediately below). | |||||||||||||
| b. | 1912–28. | |||||||||||||
| c. | Chongqing served as capital during the Second Sino-Japanese and Pacific Wars (1937–46). | |||||||||||||
| Populations from http://www.populstat.info/Asia/chinac.htm | ||||||||||||||
| Republic of China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

"Republic of China" in Traditional (top) and Simplified (bottom) Chinese characters
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Chunghwa Minkuo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | Middle or Central State | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tibetan name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tibetan | ཀྲུང་ཧྭ་དམངས་གཙོའི། ་རྒྱལ་ཁབ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhuang name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Zhuang | Cunghvaz Minzgoz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic |
Дундад иргэн улс
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠳᠤᠮᠳᠠᠳᠤ ᠢᠷᠭᠡᠨ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uyghur name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uyghur |
جۇڭخۇا مىنگو
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manchu script | ᡩᡠᠯᡳᠮᠪᠠᡳ ᡳᡵᡤᡝᠨ ᡤᡠᡵᡠᠨ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romanization | Dulimbai irgen' gurun | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Republic of China was a sovereign state in East Asia, that occupied the territories of modern China, and for part of its history Mongolia and Taiwan. It was founded in 1912, after the Qing dynasty, the last imperial dynasty, was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. The Republic's first president, Sun Yat-sen, served only briefly before handing over the position to Yuan Shikai, former leader of the Beiyang Army. His party, then led by Song Jiaoren, won the parliamentary election held in December 1912. Song was assassinated shortly after, and the Beiyang Army led by Yuan Shikai maintained full control of the government in Beijing. Between late 1915 and early 1916, Yuan tried to reinstate the monarchy, before resigning after popular unrest. After Yuan's death in 1916, members of cliques in the former Beiyang Army claimed their autonomy and clashed with each other. During this period, the authority of the republican government was weakened by a restoration of the Qing government.
In 1925, Sun's Kuomintang established a rival government in the southern city of Guangzhou together with the fledgling Communist Party of China. The economy of the north, overtaxed to support warlord adventurism, collapsed in 1927–28. General Chiang Kai-shek, who became KMT leader after Sun's death, started his military Northern Expedition campaign in order to overthrow the government in Beijing. The government was overthrown in 1928 and Chiang established a new nationalist government in Nanjing. In April 1927, he massacred the communists in Shanghai, which forced the communists into armed rebellion, marking the beginning of the Chinese Civil War.
...
Wikipedia