PIP-II
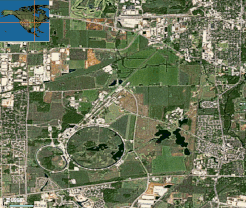
A satellite view of Fermilab. The two circular structures are the Main Injector Ring (smaller) and Tevatron (larger).
|
|
| Established | November 21, 1967 (as National Accelerator Laboratory) |
|---|---|
| Research type | Accelerator physics |
| Budget | $345 million (2015) |
|
Field of research
|
Accelerator physics |
| Director | Nigel S. Lockyer |
| Address | P.O. Box 500 |
| Location |
Winfield Township, DuPage County, Illinois, United States 41°49′55″N 88°15′26″W / 41.83194°N 88.25722°WCoordinates: 41°49′55″N 88°15′26″W / 41.83194°N 88.25722°W |
| Nickname | Fermilab |
| Affiliations |
U.S. Department of Energy University of Chicago Universities Research Association |
| Leon Max Lederman | |
| Website | www |
| Map | |
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been operated by the Fermi Research Alliance, a joint venture of the University of Chicago, and the Universities Research Association (URA). Fermilab is a part of the Illinois Technology and Research Corridor.
Fermilab's Tevatron was a landmark particle accelerator; until the startup in 2008 of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, it was the most powerful particle accelerator in the world, accelerating antiprotons to energies of 500 GeV, and producing proton-proton collisions with energies of up to 1.6 TeV, the first accelerator to reach one "tera-electron-volt" energy. At 3.9 miles (6.3 km), it was the world's fourth-largest particle accelerator in circumference. One of its most important achievements was the 1995 discovery of the top quark, announced by research teams using the Tevatron's CDF and DØ detectors. It was shut down in 2011.
In addition to high-energy collider physics, Fermilab hosts fixed-target and neutrino experiments, such as MicroBooNE (Micro Booster Neutrino Experiment), NOνA (NuMI Off-Axis νe Appearance) and SeaQuest. Completed neutrino experiments include MINOS (Main Injector Neutrino Oscillation Search), MINOS+, MiniBooNE and SciBooNE (SciBar Booster Neutrino Experiment). The MiniBooNE detector was a 40-foot (12 m) diameter sphere containing 800 tons of mineral oil lined with 1,520 phototube detectors. An estimated 1 million neutrino events were recorded each year. SciBooNE sat in the same neutrino beam as MiniBooNE but had fine-grained tracking capabilities. The NOνA experiment uses, and the MINOS experiment used, Fermilab's NuMI (Neutrinos at the Main Injector) beam, which is an intense beam of neutrinos that travels 455 miles (732 km) through the Earth to the Soudan Mine in Minnesota and the Ash River, Minnesota, site of the NOνA far detector.
...
Wikipedia

