Large Hadron Collider
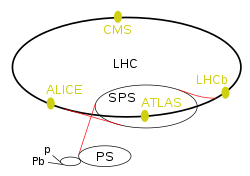 |
|
| LHC experiments | |
|---|---|
| ATLAS | A Toroidal LHC Apparatus |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| LHCb | LHC-beauty |
| ALICE | A Large Ion Collider Experiment |
| TOTEM | Total Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation |
| LHCf | LHC-forward |
| MoEDAL | Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC |
| LHC preaccelerators | |
| p and Pb | Linear accelerators for protons (Linac 2) and Lead (Linac 3) |
| (not marked) | Proton Synchrotron Booster |
| PS | Proton Synchrotron |
| SPS | Super Proton Synchrotron |
| Intersecting Storage Rings | CERN, 1971–1984 |
|---|---|
| Super Proton Synchrotron | CERN, 1981–1984 |
| ISABELLE | BNL, cancelled in 1983 |
| Tevatron | Fermilab, 1987–2011 |
| Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider | BNL, 2000–present |
| Superconducting Super Collider | Cancelled in 1993 |
| Large Hadron Collider | CERN, 2009–present |
| Future Circular Collider | Proposed |
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and most powerful particle collider, most complex experimental facility ever built, and the largest single machine in the world. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and engineers from over 100 countries, as well as hundreds of universities and laboratories. It lies in a tunnel 27 kilometres (17 mi) in circumference, as deep as 175 metres (574 ft) beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva, Switzerland. Its first research run took place from 30 March 2010 to 13 February 2013 at an initial energy of 3.5 teraelectronvolts (TeV) per beam (7 TeV total), almost 4 times more than the previous world record for a collider, rising to 4 TeV per beam (8 TeV total) from 2012. On 13 February 2013 the LHC's first run officially ended, and it was shut down for planned upgrades. 'Test' collisions restarted in the upgraded collider on 5 April 2015, reaching 6.5 TeV per beam on 20 May 2015 (13 TeV total, the current world record). Its second research run commenced on schedule, on 3 June 2015.
The aim of the LHC is to allow physicists to test the predictions of different theories of particle physics, including measuring the properties of the Higgs boson and searching for the large family of new particles predicted by supersymmetric theories, as well as other unsolved questions of physics.
The collider has four crossing points, around which are positioned seven detectors, each designed for certain kinds of research. The LHC primarily collides proton beams, but it can also use beams of lead nuclei. Proton–lead collisions were performed for short periods in 2013 and 2016, and lead–lead collisions took place in 2010, 2011, 2013, and 2015.
The LHC's computing grid is a world record holder. Data from collisions was produced at an unprecedented rate for the time of first collisions, tens of petabytes per year, a major challenge at the time, to be analysed by a grid-based computer network infrastructure connecting 140 computing centres in 35 countries – by 2012 the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid was also the world's largest distributed computing grid, comprising over 170 computing facilities in a worldwide network across 36 countries.
...
Wikipedia
