Compact Muon Solenoid
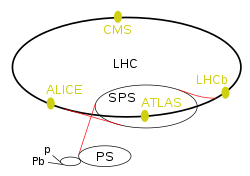 |
|
| LHC experiments | |
|---|---|
| ATLAS | A Toroidal LHC Apparatus |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| LHCb | LHC-beauty |
| ALICE | A Large Ion Collider Experiment |
| TOTEM | Total Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation |
| LHCf | LHC-forward |
| MoEDAL | Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC |
| LHC preaccelerators | |
| p and Pb | Linear accelerators for protons (Linac 2) and Lead (Linac 3) |
| (not marked) | Proton Synchrotron Booster |
| PS | Proton Synchrotron |
| SPS | Super Proton Synchrotron |
Coordinates: 46°18′34″N 6°4′37″E / 46.30944°N 6.07694°E
The Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiment is one of two large general-purpose particle physics detectors built on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Switzerland and France. The goal of CMS experiment is to investigate a wide range of physics, including the search for the Higgs boson, extra dimensions, and particles that could make up dark matter.
CMS is 21.6 metres long, 15 m in diameter, and weighs about 14,000 tonnes. Approximately 3,800 people, representing 199 scientific institutes and 43 countries, form the CMS collaboration who built and now operate the detector. It is located in an underground cavern at Cessy in France, just across the border from Geneva. In July 2012, along with ATLAS, CMS tentatively discovered the Higgs boson.
Recent collider experiments such as the now-dismantled Large Electron-Positron Collider and the newly renovated Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN, as well as the (as of October 2011[update]) recently closed Tevatron at Fermilab have provided remarkable insights into, and precision tests of, the Standard Model of Particle Physics. A principle achievement of these experiments (specifically of the LHC) is the discovery of a particle consistent with the Standard Model Higgs boson, the particle resulting from the Higgs mechanism, which provides an explanation for the masses of elementary particles.
...
Wikipedia
