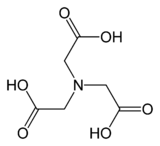
Nitrilotriacetic acid
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
2,2',2''-Nitrilotriacetic acid
|
|
| Other names
N,N-Bis(carboxymethyl)glycine
2-[Bis(carboxymethyl)amino]acetic acid Triglycine |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
139-13-9 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image Interactive image |
| 1710776 | |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:44557 |
| ChemSpider |
8428 |
| DrugBank |
DB03040 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.869 |
| EC Number | 205-355-7 |
| 3726 | |
| KEGG |
C14695 |
| MeSH | Nitrilotriacetic+Acid |
| PubChem | 8758 |
| RTECS number | AJ0175000 |
| UN number | 2811 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H9NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 191.14 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 246 °C (475 °F; 519 K) |
| Insoluble. <0.01 g/100 mL at 23℃ | |
| Thermochemistry | |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−1.3130–−1.3108 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |
 
|
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| H302, H319, H351 | |
| P281, P305+351+338 | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R22, R36, R40 |
| S-phrases | S26, S36/37/39, S45 |
| Flash point | 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
1.1 g kg−1(oral, rat) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related alkanoic acids
|
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) is the aminopolycarboxylic acid with the formula N(CH2CO2H)3. It is a colourless solid that is used as a chelating agent, which forms coordination compounds with metal ions (chelates) such as Ca2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+.
Nitrilotriacetic acid is commercially available as the free acid and as the sodium salt. It is produced from ammonia, formaldehyde, and sodium cyanide or hydrogen cyanide. Worldwide capacity is estimated at 100 thousand tonnes per year. NTA is also cogenerated as an impurity in the synthesis of EDTA, arising from reactions of the ammonia coproduct.
NTA is a tripodal tetradentate trianionic ligand.
The uses of NTA are similar to those of EDTA, both being chelating agents. It is used for water softening and as a replacement to sodium and potassium triphosphate in detergents, and cleansers.
In one application, NTA as a chelating agent removes Cr, Cu, and As from wood that had been treated with chromated-copper arsenate (CCA). .
In the laboratory, this compound is used in complexometric titrations. A variant of NTA is used for protein isolation and purification in the His-tag method. The modified NTA is used to immobilize nickel to a solid support. This allows purification of proteins containing a tag consisting of six histidine residues at either terminus.
Three views of the structure of [Ni(NTA)(H2O)2]−.
Structure of the anion [Ca(NTA)(H2O)3]−.
In contrast to EDTA, NTA is easily biodegradable and is almost completely removed during wastewater treatment. The environmental impacts of NTA are minimal. Despite widespread use in cleaning products, the concentration in the water supply is too low to have a sizeable impact on human health or environmental quality.
...
Wikipedia
