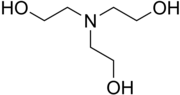
Triethanolamine
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
2,2',2''-Nitrilotri(ethan-1-ol)
|
|
Other names
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
102-71-6 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 3DMet | B01049 |
| 1699263 | |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:28621 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL446061 |
| ChemSpider |
13835630 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.773 |
| EC Number | 203-049-8 |
| KEGG |
D00215 |
| MeSH | Biafine |
| PubChem | 7618 |
| RTECS number | KL9275000 |
| UNII |
9O3K93S3TK |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C6H15NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 149.19 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Ammoniacal |
| Density | 1.124 g mL−1 |
| Melting point | 21.60 °C; 70.88 °F; 294.75 K |
| Boiling point | 335.40 °C; 635.72 °F; 608.55 K |
| 149 g L−1 (at 20 °C) | |
| log P | −0.988 |
| Vapor pressure | 1 Pa (at 20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 7.74 |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 280 nm |
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.485 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| 389 J K−1 mol−1 | |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
−665.7 – −662.7 kJ mol−1 |
|
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH |
−3.8421 – −3.8391 MJ mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| D03AX12 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | hazard.com |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| H319 | |
| P305+351+338 | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 179 °C (354 °F; 452 K) |
| 325 °C (617 °F; 598 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.3–8.5% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
|
| Related compounds | |
|
Related alkanols
|
|
|
Related compounds
|
Diethylhydroxylamine |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Triethanolamine, often abbreviated as TEA, is a viscous organic compound that is both a tertiary amine and a triol. A triol is a molecule with three alcohol groups. Triethanolamine is a strong base. Triethanolamine can also be abbreviated as TEOA, which can help to distinguish it from triethylamine. Approximately 150,000 tonnes were produced in 1999. It is a colourless compound although samples may appear yellow because of impurities.
Triethanolamine is produced from the reaction of ethylene oxide with aqueous ammonia, also produced are ethanolamine and diethanolamine. The ratio of the products can be controlled by changing the stoichiometry of the reactants.
Triethanolamine is used primarily as an emulsifier and surfactant. It is a common ingredient in formulations used for both industrial and consumer products. The triethanolamine neutralizes fatty acids, adjusts and buffers the pH, and solubilizes oils and other ingredients that are not completely soluble in water. Some common products in which triethanolamine is found are liquid laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, general cleaners, hand sanitizers, polishes, metalworking fluids, paints, shaving cream and printing inks.
...
Wikipedia

