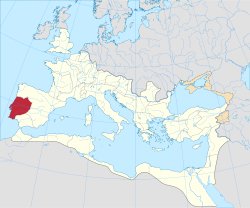
Lusitânia
| Provincia·Hispania·Lusitania | |||||
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||
|
|||||
| Capital | Emerita Augusta (Mérida) | ||||
| Historical era | Roman Empire | ||||
| • | Established | 27 BC | |||
| • | Disestablished | 891 AD | |||
| Today part of |
|
||||
Lusitania (/ˌluːsɪˈteɪniə/, Portuguese: Lusitânia, Spanish: Lusitania) or Hispania Lusitana was an ancient Iberian Roman province including approximately all of modern Portugal south of the Douro river and part of modern Spain (the present autonomous community of Extremadura and a small part of the province of Salamanca). It was named after the Lusitani or Lusitanian people (an Indo-European people). Its capital was Emerita Augusta (currently Mérida, Spain), and it was initially part of the Roman Republic province of Hispania Ulterior, before becoming a province of its own in the Roman Empire. Romans first came to the territory around the mid 2nd century BC. A war with Lusitanian tribes followed, from 155 to 139 BC. In 27 BC, the province was created.
The etymology of the name of the Lusitani (who gave the Roman province their name) remains unclear. Popular etymology connected the name to a supposed Roman demigod Lusus, whereas some early-modern scholars suggested that Lus was a form of the Celtic Lugus followed by another (unattested) root *tan-, supposed to mean "tribe", while others derived the name from Lucis, an ancient people mentioned in Avienus' Ora Maritima (4th century CE) and from tan (-stan in Iranian), or from tain, meaning "a region" or implying "a country of waters", a root word that formerly meant a prince or sovereign governor of a region.
...
Wikipedia