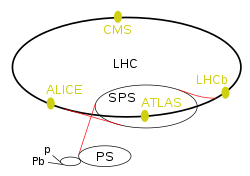
LHCb experiment
 |
|
| LHC experiments | |
|---|---|
| ATLAS | A Toroidal LHC Apparatus |
| CMS | Compact Muon Solenoid |
| LHCb | LHC-beauty |
| ALICE | A Large Ion Collider Experiment |
| TOTEM | Total Cross Section, Elastic Scattering and Diffraction Dissociation |
| LHCf | LHC-forward |
| MoEDAL | Monopole and Exotics Detector At the LHC |
| LHC preaccelerators | |
| p and Pb | Linear accelerators for protons (Linac 2) and Lead (Linac 3) |
| (not marked) | Proton Synchrotron Booster |
| PS | Proton Synchrotron |
| SPS | Super Proton Synchrotron |
Coordinates: 46°14′27.64″N 6°5′48.96″E / 46.2410111°N 6.0969333°E
The LHCb (standing for "Large Hadron Collider beauty") experiment is one of seven particle physics detector experiments collecting data at the Large Hadron Collider accelerator at CERN. LHCb is a specialized b-physics experiment, that is measuring the parameters of CP violation in the interactions of b-hadrons (heavy particles containing a bottom quark). Such studies can help to explain the Matter-Antimatter asymmetry of the Universe. The detector is also able to perform measurements of production cross sections and electroweak physics in the forward region. Approximately 840 people from 60 scientific institutes, representing 16 countries, form the collaboration who built and operate the detector. As of 2017, the spokesperson for the collaboration is Giovanni Passaleva. The experiment is located at point 8 on the LHC tunnel close to Ferney-Voltaire, France just over the border from Geneva. The (small) MoEDAL experiment shares the same cavern.
The experiment has wide physics program covering many important aspects of Heavy Flavor (both beauty and charm), Electroweak and QCD physics. Six key measurements have been identified involving B mesons. These are described in a roadmap document that form the core physics programme for the first high energy LHC running in 2010–2012. They include:
...
Wikipedia
