Chicória
| Common chicory | |
|---|---|
 |
|
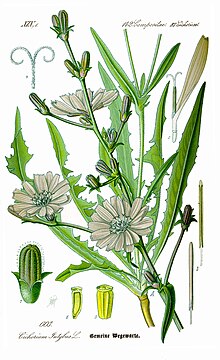
| 1885 illustration | |
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Cichorium |
| Species: | C. intybus |
| Binomial name | |
|
Cichorium intybus L. |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Synonymy
|
|
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 96 kJ (23 kcal) |
|
4.7 g
|
|
| Sugars | 0.7 g |
| Dietary fiber | 4 g |
|
0.3 g
|
|
|
1.7 g
|
|
| Vitamins | |
| Vitamin A equiv. |
(36%)
286 μg
(32%)
3430 μg10300 μg
|
| Thiamine (B1) |
(5%)
0.06 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(8%)
0.1 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(3%)
0.5 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
(23%)
1.159 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(8%)
0.105 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(28%)
110 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(29%)
24 mg |
| Vitamin E |
(15%)
2.26 mg |
| Vitamin K |
(283%)
297.6 μg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium |
(10%)
100 mg |
| Iron |
(7%)
0.9 mg |
| Magnesium |
(8%)
30 mg |
| Manganese |
(20%)
0.429 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(7%)
47 mg |
| Potassium |
(9%)
420 mg |
| Sodium |
(3%)
45 mg |
| Zinc |
(4%)
0.42 mg |
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 71 kJ (17 kcal) |
|
4 g
|
|
| Dietary fiber | 3.1 g |
|
0.1 g
|
|
|
0.9 g
|
|
| Vitamins | |
| Thiamine (B1) |
(5%)
0.062 mg |
| Riboflavin (B2) |
(2%)
0.027 mg |
| Niacin (B3) |
(1%)
0.16 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
(3%)
0.145 mg |
| Vitamin B6 |
(3%)
0.042 mg |
| Folate (B9) |
(9%)
37 μg |
| Vitamin C |
(3%)
2.8 mg |
| Minerals | |
| Calcium |
(2%)
19 mg |
| Iron |
(2%)
0.24 mg |
| Magnesium |
(3%)
10 mg |
| Manganese |
(5%)
0.1 mg |
| Phosphorus |
(4%)
26 mg |
| Potassium |
(4%)
211 mg |
| Sodium |
(0%)
2 mg |
| Zinc |
(2%)
0.16 mg |
|
|
|
|
|
| Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. Source: USDA Nutrient Database |
|
Common chicory, Cichorium intybus, is a somewhat woody, perennial herbaceous plant of the dandelion family Asteraceae, usually with bright blue flowers, rarely white or pink. Many varieties are cultivated for salad leaves, chicons (blanched buds), or roots (var. sativum), which are baked, ground, and used as a coffee substitute and additive. It is also grown as a forage crop for . It lives as a wild plant on roadsides in its native Europe, and is now common in North America, China, and Australia, where it has become widely naturalized. "Chicory" is also the common name in the United States for curly endive (Cichorium endivia); these two closely related species are often confused.
Common chicory is also known as blue daisy, blue dandelion, blue sailors, blue weed, bunk, coffeeweed, cornflower, hendibeh, horseweed, ragged sailors, succory, wild bachelor's buttons, and wild endive. (Note: "Cornflower" is commonly applied to Centaurea cyanus.) Common names for varieties of var. foliosum include endive, radicchio, radichetta, Belgian endive, French endive, red endive, sugarloaf, and witloof (or witlof).
When flowering, chicory has a tough, grooved, and more or less hairy stem, from 30 to 100 cm (10 to 40 in) tall. The leaves are stalked, lanceolate and unlobed. The flower heads are 2 to 4 cm (¼ to 1½ inches) wide, and usually light purple or lavender (see picture) and it has been described as light blue, rarely white or pink. Of the two rows of involucral bracts, the inner is longer and erect, the outer is shorter and spreading. It flowers from July until October. The achenes have no pappus (feathery hairs), but do have toothed scales on top.
...
Wikipedia
