1887 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1887 Atlantic hurricane season |

Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
May 15, 1887 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 12, 1887 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
Seven |
| • Maximum winds |
125 mph (205 km/h) |
| • Lowest pressure |
946 mbar (hPa; 27.94 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
19 |
| Total storms |
19 |
| Hurricanes |
11 |
Major hurricanes
(Cat. 3+) |
2 |
| Total fatalities |
2+ total |
| Total damage |
Unknown |
|
|
Atlantic hurricane seasons
1885, 1886, 1887, 1888, 1889
|
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 15 – May 18 |
| Peak intensity |
70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) ≤997 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 17 – May 21 |
| Peak intensity |
60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) ≤1002 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
June 12 – June 14 |
| Peak intensity |
40 mph (65 km/h) (1-min) 1004 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 20 – July 28 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) 981 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 30 – August 8 |
| Peak intensity |
60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) 1001 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 14 – August 22 |
| Peak intensity |
120 mph (195 km/h) (1-min) ≤967 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 18 – August 27 |
| Peak intensity |
125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min) 946 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 1 – September 4 |
| Peak intensity |
105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) 963 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 11 – September 22 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
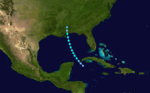
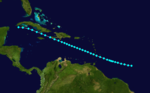
The 1887 Atlantic hurricane season was the third most active Atlantic hurricane season on record, tying with the 1995, 2010, 2011, and the 2012 seasons for third most number of storms. The season ran through the summer and almost all of the fall in 1887, and was surpassed in total number of tropical cyclones only by the seasons of 1933 and the record-breaking 2005. The 1887 season saw tropical activity as early as May, and as late as December. Tropical cyclones that did not approach populated areas or shipping lanes, especially if they were relatively weak and of short duration, may have remained undetected. Because technologies such as satellite monitoring were not available until the 1960s, historical data on tropical cyclones from this period may not be comprehensive. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated. Of the known 1887 cyclones, Tropical Storm One and Tropical Storm Three were first documented in 1996 by Jose Fernandez-Partagas and Henry Diaz. They also proposed large alterations to the known tracks of several of the other 1887 storms. Later re-analysis led to the known duration of Hurricane Six, and also that of Hurricane Fifteen, being increased.
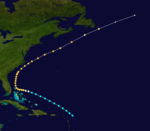
Ten of the season's nineteen known storms attained hurricane status. However, only two of these storms became major hurricanes, with sustained winds of over 111 mph (179 km/h); the strongest reached peak winds of 125 mph (205 km/h), with a minimum barometric pressure of 946 mbar (27.9 inHg) off the East Coast of the United States in late August. Only a few of the storms during the 1887 season did not impact land, but there was a low number of deaths.
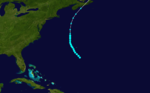
The first storm of the season formed south of Bermuda on May 15, outside of the season boundaries and moved to the northwest, staying out to sea. After peaking at 70 mph (110 km/h) late the next day, it turned northward, and became extratropical on May 18 over Newfoundland.
...
Wikipedia