1885 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1885 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
Season summary map
|
|
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | August 7, 1885 (Hurricane One) |
| Last system dissipated | October 13, 1885 (Tropical Storm Eight) |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Two |
| • Maximum winds | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 953 mbar (hPa; 28.14 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total storms | 8 |
| Hurricanes | 6 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) |
0 |
| Total fatalities | 25 |
| Total damage | $1.806 million (1885 USD) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 7 – August 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 981 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 21 – August 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 953 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 29 – August 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 17 – September 23 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) 973 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 18 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) ≤ 999 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 24 – October 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 80 mph (130 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 26 – September 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 90 mph (150 km/h) (1-min) 982 mbar (hPa) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 10 – October 13 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min) 988 mbar (hPa) |
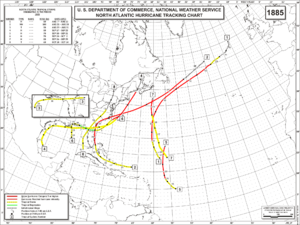
The 1885 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1885. This is the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. In 1885 there were two tropical storms and six hurricanes in the Atlantic basin. However, in the absence of modern satellite monitoring and remote-sensing technologies, only storms that affected populated land areas or encountered ships at sea were recorded, so the actual total could be higher. An undercount bias of zero to six tropical cyclones per year between 1851 and 1885 and zero to four per year between 1886 and 1910 has been estimated.
The Atlantic hurricane database (HURDAT) recognizes eight tropical cyclones for 1885 in the Atlantic basin; two were tropical storms and six were hurricanes. The most significant storm of the season was Hurricane Two, which hit Georgia as a Category 2 hurricane, causing 25 deaths.The first cyclone was a tropical storm that existed in the Atlantic between August 7 and August 13 without making landfall. From north of Puerto Rico, Hurricane Two struck the Bahamas but then remained offshore until making a landfall in South Carolina. The hurricane caused considerable damage throughout the Carolinas, Georgia and Maryland. Also in August, Tropical Storm Three formed in the Gulf of Mexico, before crossing Florida and dissipating off South Carolina. Hurricane Four also grew from a tropical storm that formed in the Gulf of Mexico. It brought high winds and flooding to towns along the Gulf coast. This storm also crossed over Florida into the Atlantic and eventually made another landfall at New Brunswick as an extratropical storm. Hurricane Five existed in the tropical Atlantic between September 18 and September 21, without making landfall. Hurricane Six formed as a tropical storm in the Gulf of Mexico and reached hurricane strength off North Carolina a week later on October 2. The cyclone had impacted both Mississippi and Florida as it had travelled north. Hurricane Seven existed in the mid-Atlantic between September 26 and September 29. The last known cyclone of 1885 was Tropical Storm Eight which formed north of Cuba and impacted Florida. It travelled through the south-east United States and brought gales and flooding to the North Carolina coast.
.
A tropical storm was seen on August 7 to the southeast of Bermuda. It moved north-northeastward, and became a hurricane on August 8. It turned to the northeast, and passed offshore of Newfoundland on the 10th as a 90 mph (145 km/h) hurricane. The hurricane weakened over the north Atlantic Ocean, and became extratropical on the 14th.
...
Wikipedia








