Ribonucleotide reductase
| ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 1.17.4.1 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9047-64-7sy | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
| ribonucleotide reductase M1 polypeptide | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RRM1 |
| Entrez | 6240 |
| HUGO | 10451 |
| OMIM | 180410 |
| RefSeq | NM_001033 |
| UniProt | P23921 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 1.17.4.1 |
| Locus | Chr. 11 p15.5-15.4 |
| ribonucleotide reductase M2 polypeptide | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RRM2 |
| Entrez | 6241 |
| HUGO | 10452 |
| OMIM | 180390 |
| RefSeq | NM_001034 |
| UniProt | P31350 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 1.17.4.1 |
| Locus | Chr. 2 p25-p24 |
| ribonucleotide reductase M2 B (TP53 inducible) | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RRM2B |
| Entrez | 50484 |
| HUGO | 17296 |
| OMIM | 604712 |
| RefSeq | NM_015713 |
| UniProt | Q9NTD8 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | EC:1.17.4.1 |
| Locus | Chr. 8 q23.1 |
| Ribonucleotide reductase N-terminal |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Crystallographic structure of the ribonucleotide reductase protein R1E from S. typhimurium. The protein is rainbow colored (N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) while dATP is depicted as sticks and a complexed magnesium ion as a grey sphere.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | RR_N | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF08343 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR013554 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1peq | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1peq | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| Ribonucleotide reductase all-alpha domain |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
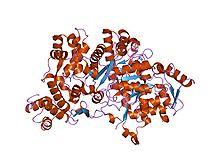
Structure of ribonucleotide reductase protein R1.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Ribonuc_red_lgN | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00317 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR013509 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00084 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1rlr | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1rlr | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| Ribonucleotide reductase barrel domain |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Structure of ribonucleotide reductase protein R1E from Salmonella typhimurium.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Ribonuc_red_lgC | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02867 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0339 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000788 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00084 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1rlr | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1rlr | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
Ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), also known as ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides. Deoxyribonucleotides in turn are used in the synthesis of DNA. The reaction catalyzed by RNR is strictly conserved in all living organisms. Furthermore, RNR plays a critical role in regulating the total rate of DNA synthesis so that DNA to cell mass is maintained at a constant ratio during cell division and DNA repair. A somewhat unusual feature of the RNR enzyme is that it catalyzes a reaction that proceeds via a free radical mechanism of action. The substrates for RNR are ADP, GDP, CDP and UDP. dTDP (deoxythymidine diphosphate) is synthesized by another enzyme (thymidylate kinase) from dTMP (deoxythymidine monophosphate).
The iron-dependent enzyme, ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), is essential for DNA synthesis. Class I RNR enzymes are constructed from large RNR1 and small RNR2 subunits which associate to form an active heterodimeric tetramer. Since the enzyme catalyses the de novo synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs), precursors to DNA synthesis, it is essential for cell proliferation.
In humans, the RNR1 subunit is encoded by the RRM1 gene while there are two isoforms of the RNR2 subunit, encoded by the RRM2 and RRM2B genes:
Each RNR1 monomer consists of three domains:
In Pfam, the second domain has been interpreted as two separate domains:
...
Wikipedia
