Methylvinylketone
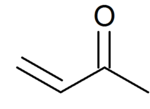 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
But-3-en-2-one
|
|
| Other names
MVK
Methylene acetone |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
78-94-4 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:48058 |
| ChemSpider |
6322 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.055 |
| PubChem | 6570 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H6O | |
| Molar mass | 70.09 g/mol |
| Density | 0.8407 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −7 °C (19 °F; 266 K) |
| Boiling point | 81.4 °C (178.5 °F; 354.5 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Methyl vinyl ketone (MVK, IUPAC name: butenone) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH=CH2. It is a reactive compound classified as an enone, in fact the simplest example thereof. It is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic liquid with a pungent odor. It is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds.
MVK has been prepared industrially by the condensation of acetone and formaldehyde, followed by dehydration. Similarly it is prepared by the Mannich reaction involving diethylammonium chloride and acetone, which produces the Mannich adduct:
Heating this ammonium salt releases the ammonium chloride and the MVK:
MVK can act as an alkylating agent because it is an effective Michael acceptor. It gained early attention for its use in the Robinson annulation, a method useful in the preparation of steroids:
Its alkylating ability is both the source of its high toxicity and the feature that makes it a useful intermediate in organic synthesis. MVK will polymerize spontaneously. The compound is typically stored with hydroquinone, which inhibits polymerization.
As an electrophilic alkene, it forms an adduct with cyclopentadiene. The resulting norbornene derivative is an intermediate in the synthesis the pesticide biperiden. Via its cyanohydrin is also a precursor to vinclozolin. It is also a precursor to synthetic vitamin A.
...
Wikipedia

