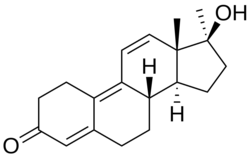
Methyltrienolone
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | Methyltrienolone, 17α-Methyltrenbolone; R-1881; RU-1881; NSC-92858; 17α-Methyl-19-nor-Δ9,11-testosterone; 17α-Methylestra-4,9,11-trien-17β-ol-3-one |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.190.113 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H24O2 |
| Molar mass | 284.393 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Metribolone (INN) (developmental code names R-1881 (or RU-1881), NSC-92858), also known as methyltrienolone (or 17α-methyltrenbolone), is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone) derivative which was never marketed for clinical use but has been used in scientific research as a photoaffinity label for the androgen receptor (AR) and in AR ligand binding assays.
Metribolone is the 17α-methylated derivative of trenbolone (trienolone), and is a similarly potent AAS, but has a high potential for hepatotoxicity similarly to other 17α-alkylated AAS. Metribolone binds with high affinity not only to the AR but also to the progesterone receptor (PR), and binds to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) as well. It has been said to be the most potent AAS.
Metribolone, also known as 17α-methyl-δ9,11-19-nortestosterone or 17α-methylestra-4,9,11-triene-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a 17α-alkylated derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone). It is closely related to normethandrone (17α-methyl-19-nortestosterone) and trenbolone (δ9,11-19-nortestosterone), as well as mibolerone (7α,17α-dimethyl-19-nortestosterone) and dimethyltrienolone (7α,17α-dimethyl-δ9,11-19-nortestosterone).
...
Wikipedia
