Hokkien language
| Hokkien | |
|---|---|
| Quanzhang | |
|
福建话/閩南語(泉漳片) Hō-ló-oē/Hô-ló-uē |
|
| Native to | China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Cambodia, Thailand, Singapore, Brunei, Malaysia, Indonesia, Philippines, United States, Madagascar, and other areas of Hoklo settlement |
| Region | southern Fujian province and other south-eastern coastal areas of Mainland China, Taiwan, Southeast Asia |
| Ethnicity | Hoklo (Subgroup of Han Chinese) |
|
Native speakers
|
37 million (date missing) |
|
Sino-Tibetan
|
|
| Dialects | |
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
None (one of the statutory languages for public transport announcements in the Taiwan) |
| Regulated by | None |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog |
hokk1242fuki1235
|

Distribution of Southern Min languages. Hokkien is dark green.
|
|
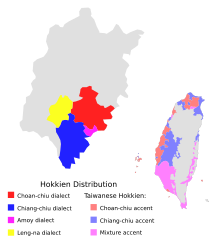
Distribution of Hokkien dialects within Fujian Province and Taiwan.
|
|
| Hokkien | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 福建話 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 福建话 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hoklo | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 福佬話 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 福佬话 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transcriptions | |
|---|---|
| Standard Mandarin | |
| Hanyu Pinyin | Fújiànhuà |
| IPA | [fǔ.tɕjɛ̂n.xwâ] |
| Wu | |
| Romanization | Foh ji ghae ho |
| Hakka | |
| Romanization | Fuk5-gien4-fa4 |
| Yue: Cantonese | |
| Yale Romanization | Fuk1-gin3-wa6 |
| Southern Min | |
| Hokkien POJ | Hok-kiàn-oē |
| Eastern Min | |
| Fuzhou BUC | Hók-gióng-uâ |
| Transcriptions | |
|---|---|
| Standard Mandarin | |
| Hanyu Pinyin | Fúlǎohuà |
| IPA | [fǔ.làu.xwâ] |
| Wu | |
| Romanization | Foh loh ghae ho |
| Hakka | |
| Romanization | Fuk5-lau3-fa4 |
| Yue: Cantonese | |
| Yale Romanization | Fuk1-lou2-wa6 |
| Southern Min | |
| Hokkien POJ | Hok-ló-oē |
| Eastern Min | |
| Fuzhou BUC | Hók-ló-uâ |
Hokkien /hɒˈkiɛn/ (from Chinese: ; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Hok-kiàn-oē) is a group of Southern Min dialects spoken throughout Southeastern China, Taiwan and Southeast Asia, and by other overseas Chinese. Hokkien originated in southern Fujian, the Min-speaking province. It is closely related to Teochew, though there is limited mutual intelligibility, and is somewhat more distantly related to Hainanese and Leizhou dialect. Besides Hokkien, there are also other Min and Hakka dialects in Fujian province, most of which are not mutually intelligible with Hokkien.
Hokkien historically served as the lingua franca amongst overseas Chinese communities of all dialects and subgroups in Southeast Asia, and remains today as the most spoken variety of Chinese in the region, including in Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia, the Philippines and some parts of Indochina.
...
Wikipedia
