Fagus grandifolia
| American beech | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Fagus |
| Species: | F. grandifolia |
| Binomial name | |
|
Fagus grandifolia Ehrh. |
|
 |
|
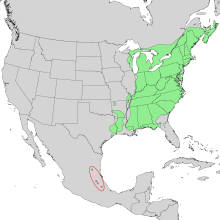
| Natural range of Fagus grandifolia | |
Fagus grandifolia (American beech or North American beech) is the species of beech tree native to the eastern United States and extreme southeast Canada. The genus name is Latin for "beech", and the species name comes from grandis "large" and folium "leaf".
The American beech is native to eastern North America, from Nova Scotia west to southern Ontario in southeastern Canada, west to Wisconsin and south to eastern Texas and northern Florida in the United States.
Trees in the southern half of the range are sometimes distinguished as a variety, F. grandifolia var. caroliniana, but this is not considered distinct in the Flora of North America. The Mexican beech (Fagus mexicana), native to the mountains of central Mexico, is closely related, and is sometimes treated as a subspecies of American beech, but more often as a distinct species. The only Fagus species found in the Western Hemisphere (assuming F. mexicana is treated as a subspecies), F. grandifolia is believed to have spanned the width of the North American continent all the way to the Pacific coast before the last ice age.
It is a deciduous tree growing to 20–35 m (66–115 ft) tall, with smooth, silver-gray bark. The leaves are dark green, simple and sparsely-toothed with small teeth that terminate each vein, 6–12 cm (2.4–4.7 in) long (rarely 15 centimetres (5.9 in)), with a short petiole. The winter twigs are distinctive among North American trees, being long and slender (15–20 mm (0.59–0.79 in) by 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in)) with two rows of overlapping scales on the buds. Beech buds are distinctly thin and long, resembling cigars; this characteristic makes beech trees relatively easy to identify. The tree is monoecious, with flowers of both sexes on the same tree. The fruit is a small, sharply-angled nut, borne in pairs in a soft-spined, four-lobed husk. It has two means of reproduction: one is through the usual dispersal of seedlings, and the other is through root sprouts (new trees sprout from the roots in different locations).
...
Wikipedia
