Borneo Island
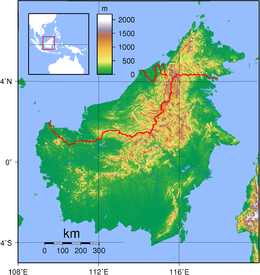
Topography of Borneo
|
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Southeast Asia |
| Coordinates | 01°N 114°E / 1°N 114°ECoordinates: 01°N 114°E / 1°N 114°E |
| Archipelago | Greater Sunda Islands |
| Area | 743,330 km2 (287,000 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 3rd |
| Highest elevation | 4,095 m (13,435 ft) |
| Highest point | Mount Kinabalu |
| Administration | |
| Districts |
Belait Brunei and Muara Temburong Tutong |
| Largest settlement | Bandar Seri Begawan (pop. ~50,000) |
| Provinces |
West Kalimantan Central Kalimantan South Kalimantan East Kalimantan North Kalimantan |
| Largest settlement | Samarinda (pop. 842,691) |
| States and FT |
Sabah Sarawak Labuan |
| Largest settlement | Kuching (pop. 617,886) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 21,258,000 (2014) |
| Pop. density | 21.52 /km2 (55.74 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Banjar, Bruneian Malay, Dayak, Iban, Kadazan-Dusun, Lun Bawang/Lun Dayeh, Murut, Rungus and Sama-Bajau |
Borneo (/ˈbɔːrnioʊ/; Malay: Pulau Borneo, Indonesian: Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and east of Sumatra.
The island is politically divided among three countries: Malaysia and Brunei in the north, and Indonesia to the south. Approximately 73% of the island is Indonesian territory. In the north, the East Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak make up about 26% of the island. Additionally, the Malaysian federal territory of Labuan is situated on a small island just off the coast of Borneo. The sovereign state of Brunei, located on the north coast, comprises about 1% of Borneo's land area. A little more than half of the island is in the Northern Hemisphere including Brunei and the Malaysian portion, while the Indonesian portion spans both the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
Antipodal to an area of Amazon rainforest, Borneo is itself home to one of the oldest rainforests in the world.
...
Wikipedia
