Anti-androgen
| Antiandrogen | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
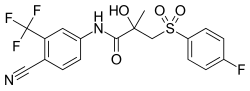
Bicalutamide, a non-steroidal antiandrogen and the most widely used androgen receptor antagonist in the treatment of prostate cancer.
|
|
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Androgen antagonists; Androgen blockers; Testosterone blockers |
| Use | Various |
| ATC code | L02BB |
| Biological target | Androgen receptor |
| Chemical class | Steroidal; Non-steroidal |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D000726 |
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs which prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the androgen receptor (AR) and/or inhibiting or suppressing androgen production. Antiandrogens are one of three types of sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiestrogens and antiprogestogens.
Antiandrogens are used to treat an assortment of androgen-dependent conditions. In males, antiandrogens are used in the treatment of prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, androgenic alopecia (pattern hair loss), hypersexuality, paraphilias, and precocious puberty. In women, antiandrogens are used to treat acne, seborrhea, hidradenitis suppurativa, hirsutism, and hyperandrogenism, such as that which occurs in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Antiandrogens are also used as a component of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for transgender women.
...
Wikipedia
