Bicalutamide
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | Bicalutamide: bye-KA-loo-TA-mide Casodex: kay-SOH-dex |
| Trade names | Casodex, Cosudex, Calutide, Calumid, Kalumid, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697047 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| Drug class | Non-steroidal antiandrogen |
| ATC code | L02BB03 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Well-absorbed; absolute bioavailability unknown |
| Protein binding |
Racemate: 96.1% (R)-Isomer: 99.6% (Mainly to albumin) |
| Metabolism |
Hepatic (extensively): • Hydroxylation (CYP3A4) • Glucuronidation (UGT1A9) |
| Metabolites | • Bicalutamide glucuronide • Hydroxybicalutamide • Hydroxybicalutamide gluc. (All inactive) |
| Biological half-life | Acute: 5.8 days Chronic: 7–10 days |
| Excretion |
Feces: 43% Urine: 34% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | ICI-176,334 |
| CAS Number |
90357-06-5 113299-40-4 ((R)-isomer) |
| PubChem (CID) | 2375 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2863 |
| DrugBank |
DB01128 |
| ChemSpider |
2284 |
| UNII |
A0Z3NAU9DP |
| KEGG |
D00961 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:3090 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL409 |
| PDB ligand ID | 198 (PDBe, RCSB PDB) |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.100 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
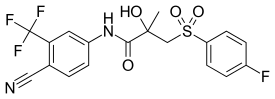
| Formula | C18H14F4N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 430.373 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| Melting point | 191 to 193 °C (376 to 379 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 0.005 mg/mL (20 °C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bicalutamide, sold under the brand name Casodex among others, is an antiandrogen that is used primarily in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is used alone or together with surgical or medical castration for this indication, and is able to slow the course of the disease and extend life. Bicalutamide is also used to treat excessive hair growth in women,early-onset puberty in boys, as a component of hormone therapy for transgender women, and in the treatment of other androgen-dependent conditions.
Bicalutamide is a non-steroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) and acts as a selective antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR), the biological target of androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It does not lower androgen levels, instead acting purely by preventing androgens from mediating their effects in the body. Bicalutamide is taken by mouth. It is well-absorbed, and its absorption is not affected by food. The drug has a long terminal half-life of 6 to 10 days. It crosses the blood–brain barrier. The major side effects of bicalutamide in men are gynecomastia (breast development), breast tenderness, and feminization in general, whereas the drug produces few side effects and is very well-tolerated in women. Bicalutamide can cause elevated liver enzymes in around 1% of people, and has been associated with a few cases of liver damage as well as lung toxicity. Although the risk is low, monitoring of liver enzymes is recommended during treatment.
...
Wikipedia
