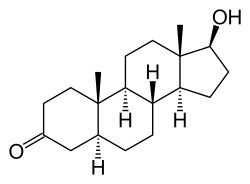
Dihydrotestosterone
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Intramuscular, transdermal |
| ATC code | A14AA01 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: 0–2% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
521-18-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 10635 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2856 |
| DrugBank |
DB02901 |
| ChemSpider |
10189 |
| UNII |
08J2K08A3Y |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:16330 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL27769 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.554 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H30O2 |
| Molar mass | 290.442 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), or 5α-dihydrotestosterone (5α-DHT), also known as 5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one, is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues including the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, epididymides, skin, hair follicles, liver, and brain. This enzyme mediates reduction of the C4-5 double bond of testosterone. Relative to testosterone, DHT is considerably more potent as an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR).
DHT has an affinity (Kd) of 0.25 to 0.5 nM for the human AR, which is about 2- to 3-fold higher than that of testosterone (Kd = 0.4 to 1.0 nM) and 15–30 times higher than that of adrenal androgens. The dissociation rate of DHT from the AR is 5-fold slower than that of testosterone. The EC50 of DHT for activation of the AR is 0.13 nM, which is about 5-fold higher than that of testosterone (EC50 = 0.66 nM). In bioassays, DHT has been found to be 2.5- to 10-fold more potent than testosterone.
...
Wikipedia
