Acacia senegal
| Acacia senegal | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. senegal |
| Binomial name | |
|
Acacia senegal (L.) Willd. |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
|
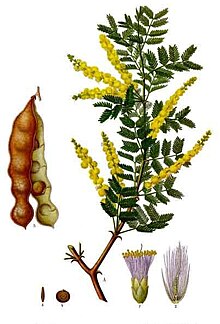
Acacia senegal (synonym: Senegalia senegal) is a small thorny deciduous tree from the genus Acacia, which is known by several common names, including Gum acacia, Gum arabic tree, Senegal gum and Sudan gum arabic. In parts of India, it is known as Kher or Khor. It is native to semi-desert regions of Sub-Saharan Africa, as well as Oman, Pakistan, west coastal India. It grows to a height of 5-12 m, with a trunk up to 30 cm in diameter.A. senegal is the source of the world's highest quality gum arabic, known locally as hashab gum in contrast to the related, but inferior, gum arabic from Red acacia or talah gum.
The tree is of great economic importance for the gum arabic it produces which is used as a food additive, in crafts, and as a cosmetic. The gum is drained from cuts in the bark, and an individual tree will yield 200 to 300 grams. Eighty percent of the world's gum arabic is produced in Sudan. The Chauhatan area of Barmer district in Rajasthan is also famous for gum production, this is called कुम्मत (Kummat) in local language there.
New foliage is very useful as forage. Leaves and pods of A. senegal are browsed by domestic and wild ruminants.
Dried seeds are used as food by humans.
Like other legume species, A. senegal fixes nitrogen within Rhizobia or nitrogen-fixing bacteria living in root nodules. This nitrogen fixation enriches the poor soils where it is grown, allowing for the rotation of other crops in naturally nutrient-poor regions.
It has been reportedly used for its astringent properties, to treat bleeding, bronchitis, cough, diarrhea, {dysentery|, catarrh, gonorrhea, leprosy, typhoid fever and upper respiratory tract infections.
...
Wikipedia
