1996 Pacific typhoon season
| 1996 Pacific typhoon season |

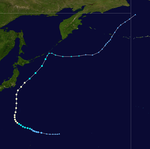
Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
February 24, 1996 |
| Last system dissipated |
December 30, 1996 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
Herb |
| • Maximum winds |
175 km/h (110 mph)
(10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure |
925 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total depressions |
43 |
| Total storms |
31 |
| Typhoons |
16 |
| Super typhoons |
6 |
| Total fatalities |
873 |
| Total damage |
$6.87 billion (1996 USD) |
| Related articles |
|
|
Pacific typhoon seasons
1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998
|
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
February 27 – March 1 |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 998 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
April 1 – April 10 |
| Peak intensity |
65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min) 1000 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical depression (JMA) |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
April 25 – April 26 |
| Peak intensity |
45 km/h (30 mph) (1-min) 1004 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 8 – May 18 |
| Peak intensity |
175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min) 930 hPa (mbar) |
| Tropical storm (JMA) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
May 18 – May 24 |
| Peak intensity |
75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min) 994 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 5 – July 12 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min) 970 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 13 – July 24 |
| Peak intensity |
155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min) 940 hPa (mbar) |
| Severe tropical storm (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 20 – July 25 |
| Peak intensity |
95 km/h (60 mph) (10-min) 975 hPa (mbar) |
| Typhoon (JMA) |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 21 – July 28 |
| Peak intensity |
120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min) 965 hPa (mbar) |
The 1996 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1996, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and west of the international date line. Storms that form east of the date line and north of the equator are called hurricanes; see 1996 Pacific hurricane season. Tropical Storms formed in the entire west pacific basin were assigned a name by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Tropical depressions in this basin have the "W" suffix added to their number. Tropical depressions that enter or form in the Philippine area of responsibility are assigned a name by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration or PAGASA. This can often result in the same storm having two names.
The 1996 season was very active. Forty-three tropical cyclones formed this year, of which 34 became tropical storms. Fifteen storms reached typhoon intensity, of which six reached super typhoon strength.
On February 23, a large area of convection developed south of the Philippines Sea. The convection developed into a low pressure area and was at first bombarded by wind shear, but conditions soon turned favorable which allowed it to strengthen rapidly on February 27 before becoming a Tropical depression later that day. The JMA upgraded 01W into a Tropical Storm before it drifted over the Philippines on February 29, and weakened slightly due to land interaction.On March 1, a cold front brought cold, dry air and vertical wind shear which pushed the system south caused the system's low level circulation center to become exposed. The exposed remnants of 01W continued to drift south, before being completely absorbed by the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
...
Wikipedia