Zinc chloride
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Zinc chloride
|
|
| Other names
Zinc(II) chloride
Zinc dichloride Butter of zinc |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
7646-85-7 Anhydrous 29426-92-4 Tetrahydrate |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:49976 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1200679 |
| ChemSpider |
5525 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.720 |
| EC Number | 231-592-0 |
| PubChem | 3007855 |
| RTECS number | ZH1400000 |
| UNII |
86Q357L16B |
| UN number | 2331 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| ZnCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.315 g/mol |
| Appearance | white crystalline solid hygroscopic and very deliquescent |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.907 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K) |
| Boiling point | 732 °C (1,350 °F; 1,005 K) |
| 432.0 g/ 1000 g (25 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, glycerol and acetone |
| Solubility in alcohol | 430.0 g/100ml |
| −65.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| Tetrahedral, linear in the gas phase | |
| Pharmacology | |
| B05XA12 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Harmful (Xn) Corrosive (C) Dangerous for the environment (N) |
| R-phrases | R22, R34, R50/53 |
| S-phrases | (S1/2), S26, S36/37/39, S45, S60, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
350 mg/kg (rat, oral) 350 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 200 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 1100 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1250 mg/kg (mouse, oral) |
|
LC50 (median concentration)
|
1260 mg/m3 (rat, 30 min) 1180 mg-min/m3 |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (fume) |
|
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 ST 2 mg/m3 (fume) |
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
50 mg/m3 (fume) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions
|
Zinc fluoride Zinc bromide Zinc iodide |
|
Other cations
|
Cadmium chloride Mercury(II) chloride |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Zinc chloride is the name of chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl2 and its hydrates. Zinc chlorides, of which nine crystalline forms are known, are colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water. ZnCl2 itself is hygroscopic and even deliquescent. Samples should therefore be protected from sources of moisture, including the water vapor present in ambient air. Zinc chloride finds wide application in textile processing, metallurgical fluxes, and chemical synthesis. No mineral with this chemical composition is known aside from the very rare mineral simonkolleite, Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O.
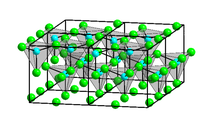
Four crystalline forms (polymorphs) of ZnCl2 are known: α, β, γ, and δ, and in each case the Zn2+ ions are tetrahedrally coordinated to four chloride ions.
Here, a, b, and c are lattice constants, Z is the number of structure units per unit cell and ρ is the density calculated from the structure parameters.
The pure anhydrous orthorhombic form (δ) rapidly changes to one of the other forms on exposure to the atmosphere and a possible explanation is that the OH− ions originating from the absorbed water facilitate the rearrangement. Rapid cooling of molten ZnCl2 gives a glass.
The covalent character of the anhydrous material is indicated by its relatively low melting point of 275 °C. Further evidence for covalency is provided by the high solubility of the dichloride in ethereal solvents where it forms adducts with the formula ZnCl2L2, where L = ligand such as O(C2H5)2. In the gas phase, ZnCl2 molecules are linear with a bond length of 205 pm.
...
Wikipedia

