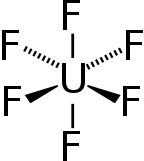
Uranium hexafluoride
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC names
Uranium hexafluoride
Uranium(VI) fluoride |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
7783-81-5 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:30235 |
| ChemSpider |
22966 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.116 |
| PubChem | 24560 |
| RTECS number | YR4720000 |
| UN number | 2978 (<1% 235U) 2977 (>1% 235U) |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| UF6 | |
| Molar mass | 352.02 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 5.09 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 64.052 °C (147.294 °F; 337.202 K) (triple point at 151 kPa) |
| Boiling point | 56.5 °C (133.7 °F; 329.6 K) (sublimes) |
| Reacts violently | |
| Solubility | soluble in chloroform, CCl4, liquid chlorine and bromine dissolves in nitrobenzene |
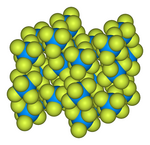
| Structure | |
| Orthorhombic, oP28 | |
| Pnma, No. 62 | |
| octahedral (Oh) | |
| 0 | |
| Thermochemistry | |
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
– solid: −430,4 ± 1,5 J·K−1·mol−1 – gaseous: −280,4 ± 1,5 J·K−1·mol−1 |
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
– solid: −(2197,7 ± 1,8) kJ·mol−1 – gaseous: −(2148,1 ± 1,8) kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 1250 |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
|
| R-phrases | R26/28, R33, R51/53 |
| S-phrases | (S1/2), S20/21, S45, S61 |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
|
Other anions
|
Uranium hexachloride |
|
Other cations
|
Neptunium hexafluoride Plutonium hexafluoride |
|
Related uranium fluorides
|
Uranium(III) fluoride Uranium(IV) fluoride Uranium(V) fluoride |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
– gaseous: −280,4 ± 1,5 J·K−1·mol−1
– gaseous: −(2148,1 ± 1,8) kJ·mol−1
Uranium hexafluoride (UF6), referred to as "hex" in the nuclear industry, is a compound used in the uranium enrichment process that produces fuel for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. It forms solid grey crystals at standard temperature and pressure, is highly toxic, reacts violently with water and is corrosive to most metals. It reacts mildly with aluminium, forming a thin surface layer of AlF3 that resists further reaction.
Milled uranium ore—U3O8 or "yellowcake"—is dissolved in nitric acid, yielding a solution of uranyl nitrate UO2(NO3)2. Pure uranyl nitrate is obtained by solvent extraction, then treated with ammonia to produce ammonium diuranate ("ADU", (NH4)2U2O7). Reduction with hydrogen gives UO2, which is converted with hydrofluoric acid (HF) to uranium tetrafluoride, UF4. Oxidation with fluorine yields UF6.
During nuclear reprocessing, uranium is reacted with chlorine trifluoride to give UF6:
At atmospheric pressure, it sublimes at 56.5 °C.
...
Wikipedia
