Sorafenib
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nexavar |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607051 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 38–49% |
| Protein binding | 99.5% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic oxidation and glucuronidation (CYP3A4 & UGT1A9-mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 25–48 hours |
| Excretion | Faeces (77%) and urine (19%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | Nexavar Sorafenib tosylate |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.110.083 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
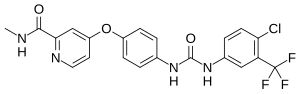
| Formula | C21H16ClF3N4O3 |
| Molar mass | 464.825 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Sorafenib (co-developed and co-marketed by Bayer and Onyx Pharmaceuticals as Nexavar), is a kinase inhibitor drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer (advanced renal cell carcinoma), advanced primary liver cancer (), and radioactive iodine resistant advanced thyroid carcinoma.
Sorafenib is a small inhibitor of several tyrosine protein kinases, such as VEGFR, PDGFR and Raf family kinases (more avidly C-Raf than B-Raf).
(See BRAF (gene)#Sorafenib for details of drug structure interaction with B-Raf.)
Sorafenib treatment induces autophagy, which may suppress tumor growth. However, autophagy can also cause drug resistance.
At the current time sorafenib is indicated as a treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC), unresectable (HCC) and thyroid cancer.
An article in The New England Journal of Medicine, published January 2007, showed that, compared with placebo, treatment with sorafenib prolongs progression-free survival in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma in whom previous therapy has failed. The median progression-free survival was 5.5 months in the sorafenib group and 2.8 months in the placebo group (hazard ratio for disease progression in the sorafenib group, 0.44; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.35 to 0.55; P<0.01). A few reports described patients with stage IV renal cell carcinomas, metastasized to the brain, that were successfully treated with a multimodal approach including neurosurgical, radiation, and sorafenib. This is one of two TGA-labelled indications for sorafenib, although it is not listed on the British Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme for this indication.
...
Wikipedia
