Sandmeyer isonitrosoacetanilide isatin synthesis
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
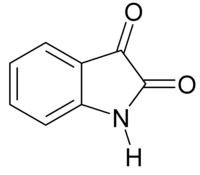
IUPAC name
1H-indole-2,3-dione
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
91-56-5 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:27539 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL326294 |
| ChemSpider |
6787 |
| DrugBank |
DB02095 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.889 |
| KEGG |
C11129 |
| PubChem | 7054 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C8H5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 147.1308 g/mol |
| Appearance | Orange-red solid |
| Melting point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Harmful (Xn) |
| R-phrases | R22 R36 R37 R38 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Isatin or 1H-indole-2,3-dione is an indole derivative. The compound was first obtained by Erdmann and Laurent in 1841 as a product from the oxidation of indigo dye by nitric acid and chromic acids. The compound is found in many plants, such as Isatis tinctoria, Calanthe discolor and in Couroupita guianensis.
Schiff bases of isatin are investigated for their pharmaceutical properties.
Isatin forms a blue dye (indophenin) if it is mixed with sulfuric acid and crude benzene. The formation of the indophenin was long believed to be a reaction with benzene. Victor Meyer was able to isolate the substance responsible for this reaction from crude benzene. This new heterocyclic compound was thiophene.
The classical methods for the synthesis of isatins are Sandmeyer’s method, the Stolle procedure, and Gassman procedure, all using aniline as substrate.
...
Wikipedia
