Benzene
|
|||
 Space-filling model
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Benzene
|
|||
| Other names
Benzol
Phene Phenyl hydride [6]annulene (not recommended) |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
71-43-2 |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:16716 |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL277500 |
||
| ChemSpider |
236 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.685 | ||
| EC Number | 200-753-7 | ||
| KEGG |
C01407 |
||
| PubChem | 241 | ||
| RTECS number | CY1400000 | ||
| UNII |
J64922108F |
||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6 | |||
| Molar mass | 78.11 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Aromatic, gasoline-like | ||
| Density | 0.8765(20) g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 5.53 °C (41.95 °F; 278.68 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 80.1 °C (176.2 °F; 353.2 K) | ||
| 1.53 g/L (0 °C) 1.81 g/L (9 °C) 1.79 g/L (15 °C) 1.84 g/L (30 °C) 2.26 g/L (61 °C) 3.94 g/L (100 °C) 21.7 g/kg (200 °C, 6.5 MPa) 17.8 g/kg (200 °C, 40 MPa) |
|||
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, CHCl3, CCl4, diethyl ether, acetone, acetic acid | ||
| Solubility in ethanediol | 5.83 g/100 g (20 °C) 6.61 g/100 g (40 °C) 7.61 g/100 g (60 °C) |
||
| Solubility in ethanol | 20 °C, solution in water: 1.2 mL/L (20% v/v) |
||
| Solubility in acetone | 20 °C, solution in water: 7.69 mL/L (38.46% v/v) 49.4 mL/L (62.5% v/v) |
||
| Solubility in diethylene glycol | 52 g/100 g (20 °C) | ||
| log P | 2.13 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 12.7 kPa (25 °C) 24.4 kPa (40 °C) 181 kPa (100 °C) |
||
| UV-vis (λmax) | 255 nm | ||
| -54.8·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5011 (20 °C) 1.4948 (30 °C) |
||
| Viscosity | 0.7528 cP (10 °C) 0.6076 cP (25 °C) 0.4965 cP (40 °C) 0.3075 cP (80 °C) |
||
| Structure | |||
| Trigonal planar | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 134.8 J/mol·K | |||
|
Std molar
entropy (S |
173.26 J/mol·K | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH |
48.7 kJ/mol | ||
|
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH |
3267.6 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | potential occupational carcinogen, flammable | ||
| Safety data sheet |
See: data page HMDB |
||
| GHS pictograms |
  
|
||
| GHS signal word | Danger | ||
| H225, H304, H315, H319, H340, H350, H372 | |||
| P201, P210, P301+310, P305+351+338, P308+313, P331 | |||
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
Carc. Cat. 1 Muta. Cat. 2 |
||
| R-phrases | R45, R46, R11, R16, R36/38,R48/23/24/25, R65 | ||
| S-phrases | S53, S45 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| Flash point | −11.63 °C (11.07 °F; 261.52 K) | ||
| 497.78 °C (928.00 °F; 770.93 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.2–7.8% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
|
LD50 (median dose)
|
930 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
|
LCLo (lowest published)
|
44,000 ppm (rabbit, 30 min) 44,923 ppm (dog) 52,308 ppm (cat) 20,000 ppm (human, 5 min) |
||
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |||
|
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 ppm, ST 5 ppm | ||
|
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca TWA 0.1 ppm ST 1 ppm | ||
|
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
500 ppm | ||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Toluene Borazine |
||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
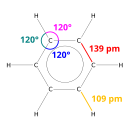
Benzene is an important organic chemical compound with the chemical formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of 6 carbon atoms joined in a ring with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Because of the cyclic continuous pi bond between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon, the second [n]-annulene ([6]-annulene). It is sometimes abbreviated Ph–H. Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is responsible for the aroma around petrol stations. It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced. Because benzene has a high octane number, it is an important component of gasoline.
Because benzene is a human carcinogen, most non-industrial applications have been limited.
The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin" (benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century as a product of southeast Asia. An acidic material was derived from benzoin by sublimation, and named "flowers of benzoin", or benzoic acid. The hydrocarbon derived from benzoic acid thus acquired the name benzin, benzol, or benzene.Michael Faraday first isolated and identified benzene in 1825 from the oily residue derived from the production of illuminating gas, giving it the name bicarburet of hydrogen. In 1833, Eilhard Mitscherlich produced it by distilling benzoic acid (from gum benzoin) and lime. He gave the compound the name benzin. In 1836, the French chemist Auguste Laurent named the substance "phène"; this word has become the root of the English word "phenol", which is hydroxylated benzene, and "phenyl", the radical formed by abstraction of a hydrogen atom (free radical H•) from benzene.
...
Wikipedia