Repaglinide
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Prandin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a600010 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 56% (oral) |
| Protein binding | >98% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic oxidation and glucuronidation (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 1 hour |
| Excretion | Fecal (90%) and renal (8%) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.190 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
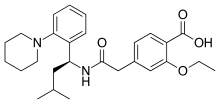
| Formula | C27H36N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 452.586 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
Repaglinide is an antidiabetic drug in the class of medications known as meglitinides, and was invented in 1983. Repaglinide is an oral medication used in addition to diet and exercise for blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. The mechanism of action of repaglinide involves promoting insulin release from β-islet cells of the pancreas; like other antidiabetic drugs, a main side effect concern is hypoglycemia. It is sold by Novo Nordisk under the name of Prandin in the U.S., GlucoNorm in Canada, Surepost in Japan, Repaglinide in Egypt by EIPICO, and NovoNorm elsewhere. In Japan it is produced by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma.
Repaglinide is an oral medication used in addition to diet and exercise for blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Repaglinide is contraindicated in people with:
Common adverse events include:
Metabolic
Respiratory
Gastrointestinal
Musculoskeletal
Other
Serious adverse events include:
Pregnancy category C: safety in pregnant women has not been established. Data is limited, and there is only one case report that notes no complications with the use of repaglinide during pregnancy.
Caution should be taken in people with liver disease and decreased kidney function when using this medication.
Repaglinide is a major substrate of CYP3A4 and should not be administered concomitantly with gemfibrozil, clarithromycin or azole antifungals such as itraconazole or . Administration of both repaglinide and one or more of these drugs results in an increase in plasma concentration of repaglinide and may lead to hypoglycemia. Co-administration of repaglinide and clopidogrel (a CYP2C8 inhibitor) may lead to a significant decrease in blood glucose levels due to a drug-drug interaction. In fact, using these drugs together for even ONE DAY can cause repaglinide levels to increase over 5-fold...and may lead to significant hypoglycemia. Repaglinide should not be combined with sulfonylurea, because they have the same mechanism of action.
...
Wikipedia
