Ovarian tumour
| Ovarian cancer | |
|---|---|
 |
|
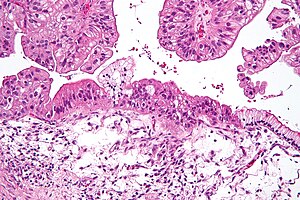
| Micrograph of a mucinous ovarian carcinoma stained by H&E. | |
| Specialty | Oncology, gynecology |
| Symptoms |
Early: vague Later: bloating, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, loss of appetite |
| Usual onset | Usual age of diagnosis 63 years old |
| Types | Ovarian carcinoma, germ cell tumor, sex cord stromal tumor |
| Risk factors | Never having children, hormone therapy after menopause, fertility medication, obesity, genetics |
| Diagnostic method | Tissue biopsy |
| Treatment | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy |
| Prognosis | Five-year survival rate ~45% (US) |
| Frequency | 1.2 million (2015) |
| Deaths | 161,100 (2015) |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Ovarian cancer is a cancer that forms in or on an ovary. It results in abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver.
The risk of ovarian cancer increases in women who have ovulated more over their lifetime. This includes those who have never had children, those who begin ovulation at a younger age or reach menopause at an older age. Other risk factors include hormone therapy after menopause, fertility medication, and obesity. Factors that decrease risk include hormonal birth control, tubal ligation, and breast feeding. About 10% of cases are related to inherited genetic risk; women with mutations in the genes BRCA1 or BRCA2 have about a 50% chance of developing the disease. The most common type of ovarian cancer, comprising more than 95% of cases, is ovarian carcinoma. There are five main subtypes of ovarian carcinoma, of which high-grade serous carcinoma is the most common. These tumors are believed to start in the cells covering the ovaries, though some may form at the Fallopian tubes. Less common types of ovarian cancer include germ cell tumors and sex cord stromal tumors. A diagnosis of ovarian cancer is confirmed through a biopsy of tissue, usually removed during surgery.
...
Wikipedia
