Peritoneum
| Peritoneum | |
|---|---|
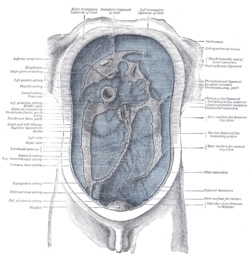
The peritoneum, colored in blue
|
|

|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Peritoneum |
| MeSH | A01.047.025.600 |
| Code | TH H3.04.08.0.00001 |
| TA | A10.1.02.002 |
| FMA | 9584 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The peritoneum /ˌpɛrᵻtəˈniːəm/ is the serous membrane that forms the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. The peritoneum supports the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves.
The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) should not be confused with the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity, but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g. the stomach), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g. the kidneys), and those structures below the intraperitoneal space are called "subperitoneal" or "infraperitoneal" (e.g. the bladder).
...
Wikipedia
