Blood vessel
| Blood vessel | |
|---|---|
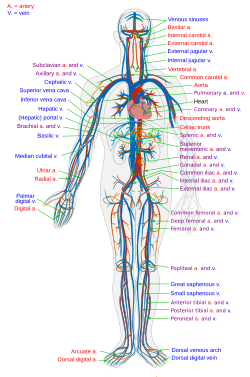
Simple diagram of the human circulatory system
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vas sanguineum |
| TA | A12.0.00.001 |
| FMA | 63183 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the human body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back toward the heart. The word vascular, meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin vas, meaning vessel. A few structures (such as cartilage and the lens of the eye) do not contain blood vessels and are labeled.
The arteries and veins have three layers, but the middle layer is thicker in the arteries than it is in the veins:
Capillaries consist of little more than a layer of endothelium and occasional connective tissue.
When blood vessels connect to form a region of diffuse vascular supply it is called an anastomosis (pl. anastomoses). Anastomoses provide critical alternative routes for blood to flow in case of blockages.
There is a layer of muscle surrounding the arteries and the veins which help contract and expand the vessels. This creates enough pressure for blood to be pumped around the body. Blood vessels are part of the circulatory system, together with the heart and the blood.
There are various kinds of blood vessels:
They are roughly grouped as arterial and venous, determined by whether the blood in it is flowing away from (arterial) or toward (venous) the heart. The term "arterial blood" is nevertheless used to indicate blood high in oxygen, although the pulmonary artery carries "venous blood" and blood flowing in the pulmonary vein is rich in oxygen. This is because they are carrying the blood to and from the lungs, respectively, to be oxygenated.
...
Wikipedia
