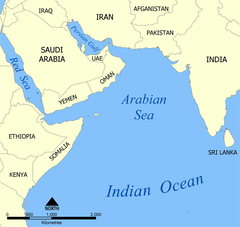
North Arabian Sea
| Arabian Sea | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Coordinates | 18°N 66°E / 18°N 66°ECoordinates: 18°N 66°E / 18°N 66°E |
| Type | Sea |
| Part of | Indian Ocean |
| Basin countries | India, Iran, Maldives, Oman, Pakistan, Somalia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen |
| Max. width | 2,400 km (1,500 mi) |
| Surface area | 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) |
| Max. depth | 4,652 m (15,262 ft) |
| Islands | Astola island, Basavaraja Durga Island, Piram Island, Pirotan, Socotra |
The Arabian Sea is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by northeastern Somalia and the Arabian Peninsula, and on the east by India. Historically the sea has been known by other names including the Erythraean Sea and the Persian Sea. Its total area is 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,000 sq mi) and its maximum depth is 4,652 metres (15,262 ft). The Gulf of Aden is in the southwest, connecting the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the strait of Bab-el-Mandeb, and the Gulf of Oman is in the northwest, connecting it to the Persian Gulf.
The Arabian Sea has been crossed by important marine trade routes since the third or second millennium BCE. Major seaports include Jawaharlal Nehru Port in Mumbai, the Port of Karachi and the Gwadar Port in Pakistan and the Port of Salalah in Oman. Other important ports include in India, Kandla Port, and Mormugao in Goa. The largest islands in the Arabian Sea include Socotra (Yemen), Masirah Island (Oman), Astola Island (Pakistan) and Andrott (India).
The Arabian Sea's surface area is about 3,862,000 km2 (1,491,130 sq mi). The maximum width of the Sea is approximately 2,400 km (1,490 mi), and its maximum depth is 4,652 metres (15,262 ft). The biggest river flowing into the Sea is the Indus River.
...
Wikipedia

