Mormoops megalophylla
| Ghost-faced bat | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Mormoopidae |
| Genus: | Mormoops |
| Species: | M. megalophylla |
| Binomial name | |
|
Mormoops megalophylla (Peters, 1864) |
|
The ghost-faced bat (Mormoops megalophylla) is a bat in the genus Mormoops. It occurs in Belize, Colombia, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Peru, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela, and Texas in the United States.Mormoops megalophylla is one of only two extant species within its genus, the other being the much smaller Mormoops blainvillii. These mammals are nocturnal and hunt using echolocation.
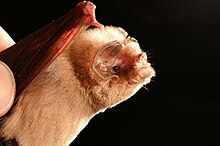
It gets its name from the unusual appearance of its face, which is due to the flaps of skin that hang from it, its poorly developed nose, and "large, round ears that join across their forehead".
The ghost-faced bat is of medium size with a reddish-brown to dark-brown appearance. The reddish color becomes more prominent as the pelage ages. This particular bat undergoes molting, usually between June and September. On the dorsal side, molting starts on the shoulders and spreads over the back, whereas on the ventral side molting usually begins under the wings, on the neck and chin and then spreads down across the abdomen.
The faces of these bats have a 'smashed-in' appearance. This odd appearance is the result of four combining factors; they do not have well-developed noses, their foreheads rise abruptly from their noses, their faces are composed of very thick dermis and muscle fibers, and they have large, round ears that seem to join across the forehead.
These bats maintain an unusually high body temperature, usually a few degrees higher than the ambient temperature. As a result, they are sensitive to temperatures under 10 °C and can only survive in these colder temperatures for a few hours before they succumb to hypothermia.
Ghost-faced bats are found in humid, arid, and semi-arid regions. They seem to prefer regions below 3000 m elevation. In the United States they have been found in southern Texas and Arizona. They have also been found in Mexico and through eastern Honduras and El Salvador. They appear to be absent in the countries of Nicaragua, Costa Rica, or Panama. Records of these bats then resume along the Caribbean coast of South America in countries such as Colombia, Venezuela, and Trinidad and Tobago. There are also records of them along the Pacific coasts in Colombia, Ecuador, and northern Peru.
...
Wikipedia

