Monarchy of Rome
| Roman Kingdom | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
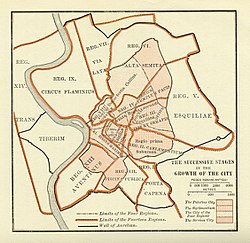
The ancient quarters of Rome.
|
||||||||||
| Capital | Rome | |||||||||
| Languages | Old Latin | |||||||||
| Religion | Roman religion | |||||||||
| Government | Elective monarchy | |||||||||
| King | ||||||||||
| • | 753–716 BC | Romulus | ||||||||
| • | 715–673 BC | Numa Pompilius | ||||||||
| • | 673–642 BC | Tullus Hostilius | ||||||||
| • | 642–616 BC | Ancus Marcius | ||||||||
| • | 616–579 BC | L. Tarquinius Priscus | ||||||||
| • | 578–535 BC | Servius Tullius | ||||||||
| • | 535–509 BC | L. Tarquinius Superbus | ||||||||
| Legislature |
Senate Roman Assemblies |
|||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | |||||||||
| • | Founding of Rome | 753 BC | ||||||||
| • | Monarchy overthrown | 509 BC | ||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Today part of |
|
|||||||||
The Roman Kingdom, or regal period, was the period of the ancient Roman civilization characterized by a monarchical form of government of the city of Rome and its territories.
Little is certain about the history of the kingdom, as nearly no written records from that time survive, and the histories about it that were written during the Republic and Empire are largely based on legends. However, the history of the Roman Kingdom began with the city's founding, traditionally dated to 753 BC with settlements around the Palatine Hill along the river Tiber in Central Italy, and ended with the overthrow of the kings and the establishment of the Republic in about 509 BC.
The site of the founding of the Roman Kingdom and eventual Republic and Empire had a ford where the Tiber could be crossed. The Palatine Hill and hills surrounding it presented easily defensible positions in the wide fertile plain surrounding them. All of these features contributed to the success of the city.
The traditional account of Roman history, which has come down to us principally through Livy, Plutarch, and Dionysius of Halicarnassus, is that in Rome's first centuries it was ruled by a succession of seven kings. The traditional chronology, as codified by Varro, allots 243 years for their reigns, an average of almost 35 years, which, since the work of Barthold Georg Niebuhr, has been generally discounted by modern scholarship. The Gauls destroyed much of Rome's historical records when they sacked the city after the Battle of the Allia in 390 BC (according to Varro; according to Polybius, the battle occurred in 387/6), and what was left was eventually lost to time or theft. With no contemporary records of the kingdom existing, all accounts of the kings must be carefully questioned.
...
Wikipedia